Spatial control of Cdc42 signalling by a GM130-RasGRF complex regulates polarity and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 25208761
- PMCID: PMC4449154
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5839
Spatial control of Cdc42 signalling by a GM130-RasGRF complex regulates polarity and tumorigenesis
Abstract
The small GTPase Cdc42 is a key regulator of polarity, but little is known in mammals about its spatial regulation and the relevance of spatial Cdc42 pools for polarity. Here we report the identification of a GM130-RasGRF complex as a regulator of Cdc42 at the Golgi. Silencing GM130 results in RasGRF-dependent inhibition of the Golgi pool of Cdc42, but does not affect Cdc42 at the cell surface. Furthermore, active Cdc42 at the Golgi is important to sustain asymmetric front-rear Cdc42-GTP distribution in directionally migrating cells. Concurrent to Cdc42 inhibition, silencing GM130 also results in RasGRF-dependent Ras-ERK pathway activation. Moreover, depletion of GM130 is sufficient to induce E-cadherin downregulation, indicative of a loss in cell polarity and epithelial identity. Accordingly, GM130 expression is frequently lost in colorectal and breast cancer patients. These findings establish a previously unrecognized role for a GM130-RasGRF-Cdc42 connection in regulating polarity and tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing financial interests exist.
Figures
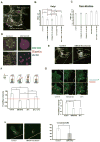
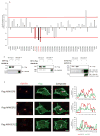
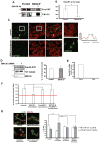
References
-
- Etienne-Manneville S. Cdc42 - the centre of polarity. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:1291–1300. - PubMed
-
- Iden S, et al. Tumor Type-Dependent Function of the Par3 Polarity Protein in Skin Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:389–403. - PubMed
-
- Erickson JW, Zhang C-j, Kahn RA, Evans T, Cerione RA. Mammalian Cdc42 Is a Brefeldin A-sensitive Component of the Golgi Apparatus. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:26850–26854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

