microRNA biogenesis, degradation and activity in plants
- PMID: 25209320
- PMCID: PMC11113746
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1728-7
microRNA biogenesis, degradation and activity in plants
Abstract
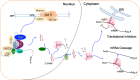
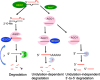
microRNAs (miRNAs) are important regulators of gene expression. After excised from primary miRNA transcript by dicer-like1 (DCL1, an RNAse III enzyme), miRNAs bind and guide their effector protein named argonaute 1 (AGO1) to silence the expression of target RNAs containing their complementary sequences in plants. miRNA levels and activities are tightly controlled to ensure their functions in various biological processes such as development, metabolism and responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. Studies have identified many factors that involve in miRNA accumulation and activities. Characterization of these factors in turn greatly improves our understanding of the processes related to miRNAs. Here, we review recent progress of mechanisms underlying miRNA expression and functions in plants.
Figures
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe D. RNA silencing in plants. Nature. 2004;431:356–363. - PubMed
-
- Bologna NG, Voinnet O (2014) The diversity, biogenesis, and activities of endogenous silencing small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:473–503 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

