Mechanisms of nanosized titanium dioxide-induced testicular oxidative stress and apoptosis in male mice
- PMID: 25209749
- PMCID: PMC4354283
- DOI: 10.1186/s12989-014-0047-3
Mechanisms of nanosized titanium dioxide-induced testicular oxidative stress and apoptosis in male mice
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Mechanisms of nanosized titanium dioxide-induced testicular oxidative stress and apoptosis in male mice.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2015 Jul 14;12:23. doi: 10.1186/s12989-015-0098-0. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26169780 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Due to the increased application of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO₂ NPs) in the food industry and daily life, their potential toxic effects in humans and animals have been investigated. However, very few studies have focused on testicular oxidative stress and/or apoptosis.
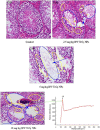
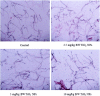
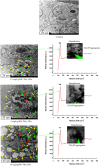
Methods: In order to understand the possible molecular mechanisms of testicular lesions following exposure to TiO₂ NPs, male mice were exposed to 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/kg body weight TiO₂ NPs for 90 consecutive days. Testicular oxidative stress and apoptosis were then evaluated, and the testicular mRNA expression of several genes and their proteins involved in oxidative stress and/or apoptosis was investigated.
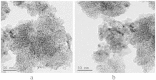
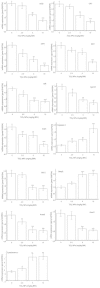
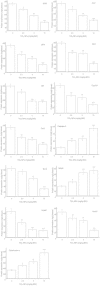
Results: TiO₂ NPs entered Sertoli cells and caused severe testicular oxidative damage and/or apoptosis, accompanied by excessive production of reactive oxygen species and peroxidation of lipids, proteins and DNA as well as a significant reduction in antioxidant capacity. Furthermore, exposure to TiO₂ NPs resulted in the up-regulation of caspase-3, Nrbp2, and cytochrome c expression, and caused down-regulation of SOD, CAT, GPx, GST, GR, Cyp1b1, Car3, Bcl-2, Acaa2, and Axud1 expression in mouse testis.
Conclusions: TiO₂ NPs entered Sertoli cells via the blood-testis barrier and were deposited in mouse seminiferous cord and/or Sertoli cells, causing oxidative damage and apoptosis.
Figures

References
-
- Lopez-Moreno ML, De La Rosa G, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL: X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) corroboration of the uptake and storage of CeO2nanoparticles and assessment of their differential toxicity in four hdible plant species.J Agric Food Chem 2010, 58:3689–3693. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

