Distinct roles of Ape1 protein, an enzyme involved in DNA repair, in high or low linear energy transfer ionizing radiation-induced cell killing
- PMID: 25210033
- PMCID: PMC4215242
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.604959
Distinct roles of Ape1 protein, an enzyme involved in DNA repair, in high or low linear energy transfer ionizing radiation-induced cell killing
Retraction in
-
Withdrawal: Distinct roles of Ape1 protein, an enzyme involved in DNA repair, in high or low linear energy transfer ionizing radiation-induced cell killing.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 1;295(18):6249. doi: 10.1074/jbc.W120.013724. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32358082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
High linear energy transfer (LET) radiation from space heavy charged particles or a heavier ion radiotherapy machine kills more cells than low LET radiation, mainly because high LET radiation-induced DNA damage is more difficult to repair. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) is the ratio of the effects generated by high LET radiation to low LET radiation. Previously, our group and others demonstrated that the cell-killing RBE is involved in the interference of high LET radiation with non-homologous end joining but not homologous recombination repair. This effect is attributable, in part, to the small DNA fragments (≤40 bp) directly produced by high LET radiation, the size of which prevents Ku protein from efficiently binding to the two ends of one fragment at the same time, thereby reducing non-homologous end joining efficiency. Here we demonstrate that Ape1, an enzyme required for processing apurinic/apyrimidinic (known as abasic) sites, is also involved in the generation of small DNA fragments during the repair of high LET radiation-induced base damage, which contributes to the higher RBE of high LET radiation-induced cell killing. This discovery opens a new direction to develop approaches for either protecting astronauts from exposure to space radiation or benefiting cancer patients by sensitizing tumor cells to high LET radiotherapy.
Keywords: Ape1; DNA Damage; DNA Damage Response; DNA Enzyme; DNA Repair; DNA-binding Protein; High LET; Radiation Biology; Radiosensitivity.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

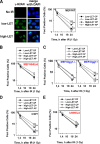
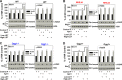

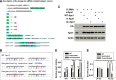

Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2021 Sep 20;86(179):52158-52160. Fed Regist. 2021. PMID: 34565929 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Heavier ions with a different linear energy transfer spectrum kill more cells due to similar interference with the Ku-dependent DNA repair pathway.Radiat Res. 2014 Oct;182(4):458-61. doi: 10.1667/RR13857.1. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 25229976 Free PMC article.
-
The Ku-dependent non-homologous end-joining but not other repair pathway is inhibited by high linear energy transfer ionizing radiation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 May 3;7(5):725-33. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.01.010. Epub 2008 Mar 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18325854
-
The repair of environmentally relevant DNA double strand breaks caused by high linear energy transfer irradiation--no simple task.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 May;17:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Feb 22. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24565812
-
Repair of DNA damage induced by accelerated heavy ions--a mini review.Int J Cancer. 2012 Mar 1;130(5):991-1000. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26445. Epub 2011 Oct 23. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21935920 Review.
-
End-processing nucleases and phosphodiesterases: An elite supporting cast for the non-homologous end joining pathway of DNA double-strand break repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Jul;43:57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.011. Epub 2016 May 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27262532 Review.
Cited by
-
A perspective on tumor radiation resistance following high-LET radiation treatment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 2;150(5):226. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05757-8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38696003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of isolated and clustered DNA damage and the post-irradiating repair process in the effects of heavy ion beam irradiation.J Radiat Res. 2015 May;56(3):446-55. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru122. Epub 2015 Feb 25. J Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 25717060 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating biomarkers to model cancer risk post cosmic ray exposure.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2016 Jun;9:19-47. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 May 21. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27345199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single low dose of Fe ions can cause long-term biological responses in NL20 human bronchial epithelial cells.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2018 Mar;57(1):31-40. doi: 10.1007/s00411-017-0719-0. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2018. PMID: 29127482
-
Prion protein deficiency impairs hematopoietic stem cell determination and sensitizes myeloid progenitors to irradiation.Haematologica. 2020 May;105(5):1216-1222. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.205716. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 31371412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeitlin C., Hassler D. M., Cucinotta F. A., Ehresmann B., Wimmer-Schweingruber R. F., Brinza D. E., Kang S., Weigle G., Böttcher S., Böhm E., Burmeister S., Guo J., Köhler J., Martin C., Posner A., Rafkin S., Reitz G. (2013) Measurements of energetic particle radiation in transit to mars on the Mars Science Laboratory, Science 340, 1080–1084 - PubMed
-
- Aufderheide E., Rink H., Hieber L., Kraft G. (1987) Heavy ion effects on cellular DNA: strand break induction and repair in cultured diploid lens epithelial cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 51, 779–790 - PubMed
-
- Rydberg B., Löbrich M., Cooper P. K. (1994) DNA double-strand breaks induced by high-energy neon and iron ions in human fibroblasts. I. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis method. Radiat. Res. 139, 133–141 - PubMed
-
- Khanna K. K., Jackson S. P. (2001) DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat. Genet. 27, 247–254 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

