Early preservation of CXCR5+ PD-1+ helper T cells and B cell activation predict the breadth of neutralizing antibody responses in chronic HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 25210168
- PMCID: PMC4249103
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02186-14
Early preservation of CXCR5+ PD-1+ helper T cells and B cell activation predict the breadth of neutralizing antibody responses in chronic HIV-1 infection
Abstract
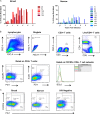
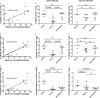
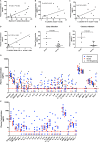
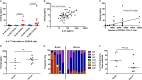
Much is known about the characteristics of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) generated during HIV-1 infection, but little is known about immunological mechanisms responsible for their development in only a minority of those infected by HIV-1. By monitoring longitudinally a cohort of HIV-1-infected subjects, we observed that the preservation of CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T helper cell frequencies and activation status of B cells during the first year of infection correlates with the maximum breadth of plasma neutralizing antibody responses during chronic infection independently of viral load. Although, during the first year of infection, no differences were observed in the abilities of peripheral CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T helper cells to induce antibody secretion by autologous naive B cells, higher frequencies of class-switched antibodies were detected in cocultures of CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T and B cells from the subjects who later developed broadly neutralizing antibody responses than those who did not. Furthermore, B cells from the former subjects had higher expression of AICDA than B cells from the latter subjects, and transcript levels correlated with the frequency of CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T cells. Thus, the early preservation of CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T cells and B cell function are central to the development of bNAbs. Our study provides a possible explanation for their infrequent generation during HIV-1 infection.
Importance: Broadly neutralizing antibodies are developed by HIV-1-infected subjects, but so far (and despite intensive efforts over the past 3 decades) they have not been elicited by immunization. Understanding how bNAbs are generated during natural HIV-1 infection and why only some HIV-1-infected subjects generate such antibodies will assist our efforts to elicit bNAbs by immunization. CXCR5(+) PD-1(+) CD4(+) T cells are critical for the development of high-affinity antigen-specific antibody responses. In our study, we found that the HIV-1-infected subjects who develop bNAbs have a higher frequency of peripheral CXCR5(+) PD-1(+) CD4(+) T cells in early infection and also that this frequency mirrored what was observed in uninfected subjects and correlated with the level of B cell activation across subjects. Our study highlights the critical role helper T cell function has in the elicitation of broadly neutralizing antibody responses in the context of HIV infection.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Binley J, Lybarger E, Crooks E, Seaman M, Gray E, Davis K, Decker J, Wycuff D, Harris L, Hawkins N, Wood B, Nathe C, Richman D, Tomaras G, Bibollet-Ruche F, Robinson J, Morris L, Shaw G, Montefiori D, Mascola J. 2008. Profiling the specificity of neutralizing antibodies in a large panel of plasmas from patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes B and C. J. Virol. 82:11651–11668. 10.1128/JVI.01762-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doria-Rose N, Klein R, Daniels M, O'Dell S, Nason M, Lapedes A, Bhattacharya T, Migueles S, Wyatt R, Korber B, Mascola J, Connors M. 2010. Breadth of human immunodeficiency virus-specific neutralizing activity in sera: clustering analysis and association with clinical variables. J. Virol. 84:1631–1636. 10.1128/JVI.01482-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nandi A, Lavine C, Wang P, Lipchina I, Goepfert P, Shaw G, Tomaras G, Montefiori D, Haynes B, Easterbrook P, Robinson J, Sodroski J, Yang X. 2010. Epitopes for broad and potent neutralizing antibody responses during chronic infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Virology 396:339–348. 10.1016/j.virol.2009.10.044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sather D, Armann J, Ching L, Mavrantoni A, Sellhorn G, Caldwell Z, Yu X, Wood B, Self S, Kalams S, Stamatatos L. 2009. Factors associated with the development of cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 83:757–769. 10.1128/JVI.02036-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simek M, Rida W, Priddy F, Pung P, Carrow E, Laufer D, Lehrman J, Boaz M, Tarragona-Fiol T, Miiro G, Birungi J, Pozniak A, McPhee D, Manigart O, Karita E, Inwoley A, Jaoko W, Dehovitz J, Bekker L, Pitisuttithum P, Paris R, Walker L, Poignard P, Wrin T, Fast P, Burton D, Koff W. 2009. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 elite neutralizers: individuals with broad and potent neutralizing activity identified by using a high-throughput neutralization assay together with an analytical selection algorithm. J. Virol. 83:7337–7348. 10.1128/JVI.00110-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

