Simultaneous determination of esculetin, quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide, quercetin-3-O-β -D-glucuronopyranside methyl ester and quercetin in effective part of Polygonum Perfoliatum L. using high performace liquid chromatography
- PMID: 25210326
- PMCID: PMC4159932
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.137379
Simultaneous determination of esculetin, quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide, quercetin-3-O-β -D-glucuronopyranside methyl ester and quercetin in effective part of Polygonum Perfoliatum L. using high performace liquid chromatography
Abstract
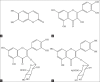
Objective: In the present study, a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with photodiode array detection was developed for simultaneous quantitation of esculetin, quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide, quercetin-3-O-β-D- glucuronopyranoside methyl ester and quercetin in Polygonum perfoliatum L.
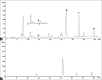
Materials and methods: The chromatographic separations were performed on a reversed-phase C18 column using a mobile phase composed of acetonitrile -0.5% aqueous acetic acid with gradient elution. The calibration curves for the analytes demonstrated good linearities within the investigated ranges. The satisfactory intra- and inter-day precision, repeatability and stability of the developed analytical method were shown in the method validation procedure. The recoveries of the established method ranged from 95.76 to 102.10% for all the analytes.
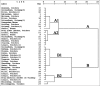
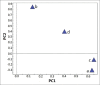
Results: This proposed method was successfully applied for simultaneous quantification of the four compounds in effective part of Polygonum perfoliatum L. from different regions. Hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA) and principal components analysis (PCA) were performed to characterize and classify the samples based on the contents of the four compounds in Polygonum perfoliatum L.
Conclusion: The established HPLC method combined with chemometric approaches was proven to be useful and efficient for quality control of Polygonum perfoliatum L.
Keywords: High performance liquid chromatography; Polygonum perfoliatum L.; diode array detector; hierarchical clustering analysis; principal components analysis; quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory, antiviral and quantitative study of quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide in Polygonum perfoliatum L.Fitoterapia. 2011 Sep;82(6):805-10. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2011.04.007. Epub 2011 May 5. Fitoterapia. 2011. PMID: 21570451
-
Quality evaluation of Polygonum multiflorum in China based on HPLC analysis of hydrophilic bioactive compounds and chemometrics.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Jan;72:223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2012.08.026. Epub 2012 Sep 10. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23021005
-
Simultaneous Determination of Eight Bioactive Compounds in Dianthus superbus by High-performance Liquid Chromatography.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 May;12(Suppl 2):S264-9. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.182159. Epub 2016 May 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27279718 Free PMC article.
-
[Quality evaluation of wildlife tending Polygonum perfoliatum].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 May;37(9):1180-3. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22803356 Chinese.
-
Quantitative Analysis and Comparison of Four Major Flavonol Glycosides in the Leaves of Toona sinensis (A. Juss.) Roemer (Chinese Toon) from Various Origins by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detector and Hierarchical Clustering Analysis.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 May;12(Suppl 2):S270-6. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.182160. Epub 2016 May 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27279719 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of Geographical Origin on the Contents of Inorganic Elements and Bioactive Compounds in Polygonum perfoliatum L.Molecules. 2025 May 21;30(10):2231. doi: 10.3390/molecules30102231. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40430408 Free PMC article.
-
Polygonum perfoliatum L., an Excellent Herbal Medicine Widely Used in China: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 16;11:581266. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.581266. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33304269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin-3-O-β-D-Glucuronide Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced JNK and ERK Phosphorylation in LPS-Challenged RAW264.7 Cells.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016 Nov 1;24(6):610-615. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.026. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016. PMID: 27257013 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide in the Ethanol Extract of Lotus Leaf (Nelumbo nucifera) Enhances Sleep Quantity and Quality in a Rodent Model via a GABAergic Mechanism.Molecules. 2021 May 19;26(10):3023. doi: 10.3390/molecules26103023. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34069439 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Mechanism of Polygonum perfoliatum L. Extract on Chronic Alcoholic Liver Injury Based on UHPLC-QExactive Plus Mass Spectrometry Lipidomics and MALDI-TOF/TOF Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Foods. 2022 May 28;11(11):1583. doi: 10.3390/foods11111583. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35681333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vol. 1. Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2010. National Commission of Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Pharmacopoeia of Peoples Republic of China; p. 155.
-
- Xinyixueyuan. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Scientific and Technologic Press; 2000. Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine; p. 869.
-
- Huang HF, Zhang CC, Yuan D, Zhou ZY. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects of Polygonum perfoliatum L. Anhui Med Pharm J. 2008;12:595–6.
-
- Long WY, Li YH. Experimental study on the effect of relieving cough and reducing sputum of Polygonum perfoliatum L. Chin J Clin Ration Drug Use. 2010;3:34–5.
-
- Fu YX, He XR, Li JC, Liu XX. Study of chemical constitution and anti-bacterial effect of Herb Polygonum perfoliatum L. Prog Vet Med. 2008;29:45–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
