Development and validation of an UPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for determination of dehydroevodiamine, limonin, evodiamine, and rutaecarpine in Evodiae Fructus
- PMID: 25210328
- PMCID: PMC4159934
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.137381
Development and validation of an UPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for determination of dehydroevodiamine, limonin, evodiamine, and rutaecarpine in Evodiae Fructus
Abstract
Objective: Evodiae Fructus (EF), one of the most widely used traditional Chinese medicines, mainly consists of alkaloids, is widely used for the treatments of headache and gastrointestinal disorders. In this study, a sensitive and reliable UPLC-ESI-MS/MS method was developed for qualitative determination of dehydroevodiamine, limonin, evodiamine, and rutaecarpine.
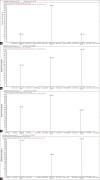
Materials and methods: Chromatographic separations were accomplished on a Phenomenex Kinetex XB-C18 column (2.1 × 150 mm, 1.7 μm) by using a gradient elution profile with a mobile phase consisting of 0.5% formic acid in water (A) and acetonitrile (B). Detection was performed using multiple reactions monitoring mode under ESI in the positive ion mode.
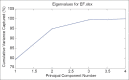
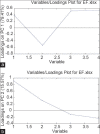
Results: The results showed good linearity over the investigated concentration ranges (R (2)>0.9900) for the analytes. The limit of quantitations (LOQs) were 6.88 ng/mL for dehydroevodiamine, 18.6 ng/mL for limonin, 6.24 ng/mL for evodiamine, and 2.56 ng/mL for rutaecarpine, respectively. Intraday and interday precisions (relative standard deviations, %) were <5% and accuracies ranged from 92% to 106%.
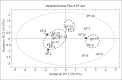
Conclusion: The validated method was successfully applied to assay the contents of the four compounds in EF samples from different regions, with which just 10 min was needed to analyze each sample.
Keywords: Evodiae Fructus; Quantitative determination; UPLC-ESI-MS/MS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- State Pharmacopoeia Committee. Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2010. Chinese Pharmacopoeia [S]
-
- Moon TC, Murakami M, Kudo I, Son KH, Kim HP, Kang SS, et al. A new class of COX-2 inhibitor, rutaecarpine from Evodia rutaecarpa. Inflamm Res. 1999;48:621–5. - PubMed
-
- Yarosh DB, Galvin JW, Nay SL, Pena AV, Canning MT, Brown DA. Anti-inflammatory activity in skin by biomimetic of Evodia rutaecarpa extract from traditional Chinese medicine. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;42:13–21. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda H, Wu JX, Tanaka T, Iinuma M, Kubo M. Antinociceptive activities of 70% methanol extract of evodiae fructus (fruit of Evodia rutaecarpa var. bodinieri) and its alkaloidal components. Biol Pharm Bull. 1997;20:243–8. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi Y. The nociceptive and anti-nociceptive effects of evodiamine from fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa in mice. Planta Med. 2003;69:425–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
