Cytoprotection "gone astray": Nrf2 and its role in cancer
- PMID: 25210464
- PMCID: PMC4155833
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S36624
Cytoprotection "gone astray": Nrf2 and its role in cancer
Abstract
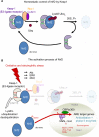
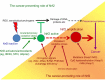
Nrf2 has gained great attention with respect to its pivotal role in cell and tissue protection. Primarily defending cells against metabolic, xenobiotic and oxidative stress, Nrf2 is essential for maintaining tissue integrity. Owing to these functions, Nrf2 is regarded as a promising drug target in the chemoprevention of diseases, including cancer. However, much evidence has accumulated that the beneficial role of Nrf2 in cancer prevention essentially depends on the tight control of its activity. In fact, the deregulation of Nrf2 is a critical determinant in oncogenesis and found in many types of cancer. Therefore, amplified Nrf2 activity has profound effects on the phenotype of tumor cells, including radio/chemoresistance, apoptosis protection, invasiveness, antisenescence, autophagy deficiency, and angiogenicity. The deregulation of Nrf2 can result from various epigenetic and genetic alterations directly affecting Nrf2 control or from the complex interplay of Nrf2 with numerous oncogenic signaling pathways. Additionally, alterations of the cellular environment, eg, during inflammation, contribute to Nrf2 deregulation and its persistent activation. Therefore, the status of Nrf2 as anti- or protumorigenic is defined by many different modalities. A better understanding of these modalities is essential for the safe use of Nrf2 as an activation target for chemoprevention on the one hand and as an inhibition target in cancer therapy on the other. The present review mainly addresses the conditions that promote the oncogenic function of Nrf2 and the resulting consequences providing the rationale for using Nrf2 as a target structure in cancer therapy.
Keywords: cancer therapy; carcinogen; transcription factor; tumorigenesis; xenobiotic and oxidative stress.
Figures

References
-
- Kang KW, Lee SJ, Kim SG. Molecular mechanism of nrf2 activation by oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7(11–12):1664–1673. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M. Toward clinical application of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013;34(6):340–346. - PubMed
-
- Giudice A, Montella M. Activation of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway: a promising strategy in cancer prevention. Bioessays. 2006;28(2):169–181. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

