An explanatory evo-devo model for the developmental hourglass
- PMID: 25210617
- PMCID: PMC4156030
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.4583.2
An explanatory evo-devo model for the developmental hourglass
Abstract
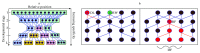
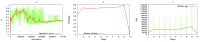
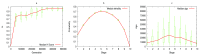
The "developmental hourglass'' describes a pattern of increasing morphological divergence towards earlier and later embryonic development, separated by a period of significant conservation across distant species (the "phylotypic stage''). Recent studies have found evidence in support of the hourglass effect at the genomic level. For instance, the phylotypic stage expresses the oldest and most conserved transcriptomes. However, the regulatory mechanism that causes the hourglass pattern remains an open question. Here, we use an evolutionary model of regulatory gene interactions during development to identify the conditions under which the hourglass effect can emerge in a general setting. The model focuses on the hierarchical gene regulatory network that controls the developmental process, and on the evolution of a population under random perturbations in the structure of that network. The model predicts, under fairly general assumptions, the emergence of an hourglass pattern in the structure of a temporal representation of the underlying gene regulatory network. The evolutionary age of the corresponding genes also follows an hourglass pattern, with the oldest genes concentrated at the hourglass waist. The key behind the hourglass effect is that developmental regulators should have an increasingly specific function as development progresses. Analysis of developmental gene expression profiles from Drosophila melanogaster and Arabidopsis thaliana provide consistent results with our theoretical predictions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures







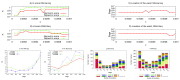


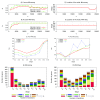


Similar articles
-
Evidence for active maintenance of phylotranscriptomic hourglass patterns in animal and plant embryogenesis.Mol Biol Evol. 2015 May;32(5):1221-31. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv012. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Mol Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25631928 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-embryo gene expression variability recapitulates the hourglass pattern of evo-devo.BMC Biol. 2020 Sep 19;18(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00842-z. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 32950053 Free PMC article.
-
The Phylotypic Brain of Vertebrates, from Neural Tube Closure to Brain Diversification.Brain Behav Evol. 2024;99(1):45-68. doi: 10.1159/000537748. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Brain Behav Evol. 2024. PMID: 38342091 Review.
-
The hourglass model of evolutionary conservation during embryogenesis extends to developmental enhancers with signatures of positive selection.Genome Res. 2021 Sep;31(9):1573-1581. doi: 10.1101/gr.275212.121. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Genome Res. 2021. PMID: 34266978 Free PMC article.
-
The developmental hourglass model: a predictor of the basic body plan?Development. 2014 Dec;141(24):4649-55. doi: 10.1242/dev.107318. Development. 2014. PMID: 25468934 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of bow-tie architectures in biology.PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Mar 23;11(3):e1004055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004055. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 25798588 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving gene regulatory networks into cellular networks guiding adaptive behavior: an outline how single cells could have evolved into a centralized neurosensory system.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jan;359(1):295-313. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2043-1. Epub 2014 Nov 23. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25416504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A transcriptomic hourglass in brown algae.Nature. 2024 Nov;635(8037):129-135. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08059-8. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39443791 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal mRNA input of growth and stress-response-related genes in cichlids in relation to egg size and trophic specialization.Evodevo. 2018 Dec 1;9:23. doi: 10.1186/s13227-018-0112-3. eCollection 2018. Evodevo. 2018. PMID: 30519389 Free PMC article.
-
The hourglass organization of the Caenorhabditis elegans connectome.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Feb 6;16(2):e1007526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007526. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32027645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raff RA: The shape of life: genes, development, and the evolution of animal form.University of Chicago Press. Trends Ecol Evol. 1996;11(10):441–442. 10.1016/0169-5347(96)81153-0 - DOI
-
- Davidson EH: The regulatory genome: gene regulatory networks in development and evolution. Academic Press, 2nd edition.2010. Reference Source
-
- Duboule D: Temporal colinearity and the phylotypic progression: a basis for the stability of a vertebrate Bauplan and the evolution of morphologies through heterochrony. Dev Suppl. 1994;1994(Supplement):135–142. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

