Interrelationships between ALOX5AP polymorphisms, serum leukotriene B4 level and risk of acute coronary syndrome
- PMID: 25210744
- PMCID: PMC4161330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106596
Interrelationships between ALOX5AP polymorphisms, serum leukotriene B4 level and risk of acute coronary syndrome
Abstract
Background: We investigated the relationships between the ALOX5AP gene rs10507391 and rs4769874 polymorphisms, serum levels of leukotriene (LT) B4, and risk of acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
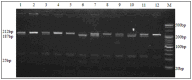
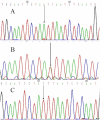
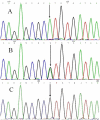
Methods: A total of 709 participants, comprising 508 ACS patients (ACS group) and 201 noncoronary artery disease patients with chest pain (control group) were recruited from the Han population of the Changwu region in China. Two polymorphic loci were genotyped using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Serum LTB4 level was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
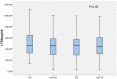
Results: Serum LTB4 levels were significantly higher (P<0.001) in the ACS group (median/interquartile range, 470.27/316.32 pg/ml) than in the control group (233.05/226.82 pg/ml). No statistical differences were observed between genotype, allele and haplotype frequencies for the tested loci in either the ACS group or the control group, even after adjustments were made for conventional risk factors by multivariate logistic regression. This suggests there is no association between the ALOX5AP rs10507391 and rs4769874 polymorphisms and ACS risk. Elevated serum LTB4 level was closely linked to ACS risk, and may be independent of traditional risk factors as a risk factor for ACS (P<0.001). There was no significant association between serum LTB4 levels and the two variants in either the ACS group or the control group.
Conclusions: Rs10507391, rs4769874 and its haplotypes in ALOX5AP are unrelated to ACS risk in the Chinese Han population of Changwu, but elevated serum LTB4 level is strongly associated with ACS risk. Serum LTB4 level is not subject to the influence of either the rs10507391, rs4769874 or the haplotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genetic variation in the leukotriene pathway is associated with myocardial infarction in the Chinese population.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Jan 24;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-0968-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30678701 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between Polymorphism in ALOX5, ALOX5AP and Susceptibility to Myeloid Leukemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Feb;28(1):40-50. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2020.01.008. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32027251 Chinese.
-
Association of ALOX5AP rs10507391/SG13S114 A>T polymorphism with cerebral infarction in the Chinese population: a meta-analysis study.Int J Neurosci. 2015;125(10):726-32. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2014.967769. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Int J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25242267
-
A tagging SNP in ALOX5AP and risk of stroke: a haplotype-based analysis among eastern Chinese Han population.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Oct;38(7):4731-8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0610-4. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21153769
-
Association of ALOX5AP haplotypes with susceptibility to coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population.Eur J Intern Med. 2012 Jul;23(5):e119-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2012.02.010. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Eur J Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22726381
Cited by
-
Genetic variation in the leukotriene pathway is associated with myocardial infarction in the Chinese population.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Jan 24;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-0968-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30678701 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of inflammation by lipid mediators in oral diseases.Oral Dis. 2017 Jul;23(5):576-597. doi: 10.1111/odi.12544. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Oral Dis. 2017. PMID: 27426637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A tagging ALOX5AP polymorphism and risk of ischemic stroke in a northeastern Chinese Han population.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Nov 15;8(11):21343-50. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26885075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maznyczka A, Braund P, Mangino M, Samani NJ (2008) Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) promoter genotype and risk of myocardial infarction: a case-control study. Atherosclerosis 199 (2): 328–332. - PubMed
-
- Helgadottir A, Manolescu A, Thorleifsson G, Gretarsdottir S, Jonsdottir H, et al. (2004) The gene encoding 5-lipoxygenase activating protein confers risk of myocardial infarction and stroke. Nat Genet 36 (3): 233–239. - PubMed
-
- Kaushal R, Pal P, Alwell K, Haverbusch M, Flaherty M, et al. (2007) Association of ALOX5AP with ischemic stroke: a population-based case-control study. Hum Genet 121 (5): 601–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

