Common genetic variants of the human steroid 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21A2) are related to differences in circulating hormone levels
- PMID: 25210767
- PMCID: PMC4161435
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107244
Common genetic variants of the human steroid 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21A2) are related to differences in circulating hormone levels
Abstract
Purpose: Systematic evaluation of the potential relationship between the common genetic variants of CYP21A2 and hormone levels.
Methods: The relationships of CYP21A2 intron 2 polymorphisms and haplotypes with diverse baseline and stimulated blood hormone levels were studied in 106 subjects with non-functioning adrenal incidentaloma (NFAI). The rationale for using NFAI subjects is dual: i) their baseline hormone profiles do not differ from those of healthy subjects and ii) hormone levels after stimulation tests are available.
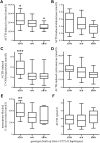
Results: The carriers (N = 27) of a well-defined CYP21A2 haplotype cluster (c5) had significantly elevated levels of cortisol (p = 0.0110), and 17-hydroxyprogesterone (p = 0.0001) after ACTH stimulation, and 11-deoxycortisol after metyrapone administration (p = 0.0017), but the hormone values were in normal ranges. In addition, the carriers (N = 33) of the C allele of the rs6462 polymorphism had a higher baseline aldosterone level (p = 0.0006). The prevalence of these genetic variants of CYP21A2 did not differ between NFAI and healthy subjects.
Conclusions: The common CYP21A2 variants presumably exert the same effect on hormone levels in the healthy and disease-affected populations. Therefore, they may contribute to complex diseases such as some cardiovascular diseases, and may influence the genotype-phenotype correlation in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) including the individual need for hormone substitution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship of CYP21A2 genotype and serum 17-hydroxyprogesterone and cortisol levels in a large cohort of Italian children with premature pubarche.Eur J Endocrinol. 2011 Aug;165(2):307-14. doi: 10.1530/EJE-11-0119. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21646284
-
Prevalence and Clinical Outcome of CYP21A2 Gene Mutations in Patients with Nonfunctional Adrenal Incidentalomas.Horm Metab Res. 2015 Aug;47(9):662-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1549911. Epub 2015 May 13. Horm Metab Res. 2015. PMID: 25970792
-
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a very rare cause of adrenal incidentalomas in Sweden.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 5;13:1017303. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1017303. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36545328 Free PMC article.
-
[From gene to disease: adrenogenital syndrome and the CYP21A2 gene].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2007 May 26;151(21):1174-7. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2007. PMID: 17557757 Review. Dutch.
-
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: An Update on Genetic Analysis of CYP21A2 Gene.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021 Jul;129(7):477-481. doi: 10.1055/a-1108-1419. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 32131114 Review.
Cited by
-
A unique haplotype of RCCX copy number variation: from the clinics of congenital adrenal hyperplasia to evolutionary genetics.Eur J Hum Genet. 2017 Jun;25(6):702-710. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2017.38. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Eur J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28401898 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenomic landscape of Indian population using whole genomes.Clin Transl Sci. 2022 Apr;15(4):866-877. doi: 10.1111/cts.13153. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Clin Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35338580 Free PMC article.
-
Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome.Endocrine. 2015 Sep;50(1):32-50. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0656-0. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Endocrine. 2015. PMID: 26082286 Review.
-
Sarcopenia and Variation in the Human Leukocyte Antigen Complex.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020 Jan 20;75(2):301-308. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glz042. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 30772894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banlaki Z, Doleschall M, Rajczy K, Fust G, Szilagyi A (2012) Fine-tuned characterization of RCCX copy number variants and their relationship with extended MHC haplotypes. Genes Immun 13: 530–535. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Mendoza AR, Welch TR, Zipf WB, Yu CY (1999) Modular variations of the human major histocompatibility complex class III genes for serine/threonine kinase RP, complement component C4, steroid 21-hydroxylase CYP21, and tenascin TNX (the RCCX module). A mechanism for gene deletions and disease associations. J Biol Chem 274: 12147–12156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

