Baseline knee adduction and flexion moments during walking are both associated with 5 year cartilage changes in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 25211281
- PMCID: PMC4369510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2014.08.009
Baseline knee adduction and flexion moments during walking are both associated with 5 year cartilage changes in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: To test the hypothesis that knee cartilage changes over 5 years are associated with baseline peak knee adduction moment (KAM) and peak knee flexion moment (KFM) during early stance.
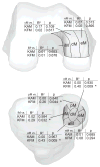
Design: Baseline KAM and KFM were measured in sixteen subjects with medial knee osteoarthritis (OA). Regional changes in cartilage thickness and changes in medial-to-lateral thickness ratio were quantified using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at baseline and again after 5 years. Multiple regression was used to determine whether baseline measures of KAM and KFM were associated with cartilage changes over 5 years. Associations with baseline pain score, Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grade, walking speed, age, gender, and body mass index (BMI) were tested one-by-one in the presence of KAM and KFM.
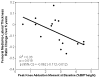
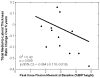
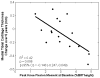
Results: Changes over 5 years in femoral medial-to-lateral thickness ratio were associated with baseline KAM, KFM, and pain score (R(2) = 0.60, P = 0.010), and most significantly with KAM (R(2) = 0.33, P = 0.019). Changes in tibial medial-to-lateral thickness ratio were associated with baseline KAM, KFM, and walking speed (R(2) = 0.49, P = 0.039), with KFM driving this association (R(2) = 0.40, P = 0.009). Changes in medial tibial thickness were associated with baseline KAM, KFM, and walking speed (R(2) = 0.49, P = 0.041); KFM also drove this association (R(2) = 0.42, P = 0.006).
Conclusions: The findings that the KAM has a greater influence on femoral cartilage change and the KFM has a greater influence on tibial cartilage change provide new insight into the tibiofemoral variations in cartilage changes associated with walking kinetics. These results suggest that both KAM and KFM should be considered when designing disease interventions as well as when assessing the risk for OA progression.
Keywords: Ambulatory mechanics; Cartilage thickness; Disease progression; Gait; Kinetics; MRI.
Copyright © 2014 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors had any conflict of interest with this study.
Figures
References
-
- Dillon CF, Rasch EK, Gu Q, Hirsch R. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the United States: arthritis data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1991–94. Journal of Rheumatology. 2006;33:2271–2279. - PubMed
-
- Jordan JM, Helmick CG, Renner JB, Luta G, Dragomir AD, Woodard J, et al. Prevalence of knee symptoms and radiographic and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in African Americans and Caucasians: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project. Journal of Rheumatology. 2007;34:172–180. - PubMed
-
- Baliunas A, Hurwitz D, Ryals A, Karrar A, Case J, Block J, et al. Increased knee joint loads during walking are present in subjects with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2002;10:573–579. - PubMed
-
- Astephen JL, Deluzio KJ. Changes in frontal plane dynamics and the loading response phase of the gait cycle are characteristic of severe knee osteoarthritis application of a multidimensional analysis technique. Clinical Biomechanics. 2005;20:209–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

