High-resolution, whole-body vascular imaging with ferumoxytol as an alternative to gadolinium agents in a pediatric chronic kidney disease cohort
- PMID: 25212105
- PMCID: PMC5911924
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-014-2953-x
High-resolution, whole-body vascular imaging with ferumoxytol as an alternative to gadolinium agents in a pediatric chronic kidney disease cohort
Abstract
Background: Exposure to gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) has been associated with the development of a potentially fatal disorder, nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF). Although contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) is an alternative to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), it carries the risk of radiation exposure and further reduction of residual renal function. Therefore we sought to assess the feasibility of ferumoxytol as an alternative to GBCA for contrast-enhanced MR angiography (MRA) in a pediatric cohort with CKD. Ferumoxytol is a parenteral iron supplement that contains ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) and is a potent relaxivity agent for MRI.
Methods: We describe the MRI findings in ten pediatric patients who needed detailed vascular mapping. Ferumoxytol (4 mg/kg) was administered intravenously for contrast-enhanced MRA. The patients tolerated the procedure without complications.
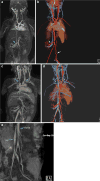
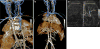
Results: Resulting studies were highly diagnostic and were pivotal in guiding patient management. The images were notable for clear delineation of multiple vascular occlusions.
Conclusions: Given the concerns associated with the use of GBCAs in renal failure, ferumoxytol is an excellent alternative contrast agent in pediatric end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. Future studies are needed in order to further evaluate safety and efficacy of ferumoxytol in this patient population.
Figures
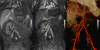
Similar articles
-
Ferumoxytol-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Late-Stage CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2016 Jun;67(6):984-8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.12.017. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 26786296 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance venography in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease: initial experience with ferumoxytol.Pediatr Radiol. 2016 Aug;46(9):1332-40. doi: 10.1007/s00247-016-3605-z. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Pediatr Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27059620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxides (USPIOs): a future alternative magnetic resonance (MR) contrast agent for patients at risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF)?Kidney Int. 2009 Mar;75(5):465-74. doi: 10.1038/ki.2008.496. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 18843256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferumoxytol-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography is a feasible method for the clinical evaluation of lower extremity arterial disease.Ann Vasc Surg. 2015 Jan;29(1):63-8. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Ann Vasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 25269682 Free PMC article.
-
Ferumoxytol magnetic resonance angiography: a dose-finding study in patients with chronic kidney disease.Eur Radiol. 2019 Jul;29(7):3543-3552. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06137-4. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30919067 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Ferumoxytol-enhanced MR Angiography and CT Angiography for the Detection of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Initial Results.Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020 Apr 30;2(2):e190077. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2020190077. eCollection 2020 Apr. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33778550 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular applications of ferumoxytol-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen and pelvis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 May;46(5):2203-2218. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02817-8. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 33090256 Review.
-
Crossover comparison of ferumoxytol and gadobenate dimeglumine for abdominal MR-angiography at 3.0 tesla: Effects of contrast bolus length and flip angle.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Jun;45(6):1617-1626. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25513. Epub 2016 Nov 10. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27862577 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ferumoxytol-enhanced ultrashort TE MRA and quantitative morphometry of the human kidney vasculature.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Jul;46(7):3288-3300. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-02984-2. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 33666735 Free PMC article.
-
Ferumoxytol-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Late-Stage CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2016 Jun;67(6):984-8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.12.017. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 26786296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hadizadeh DR, Kukuk GM, Fahlenkamp UL, Pressacco J, Schafer C, Rabe E, Koscielny A, Verrel F, Schild HH, Willinek WA. Simultaneous MR arteriography and venography with blood pool contrast agent detects deep venous thrombosis in suspected arterial disease. Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198:1188–1195. - PubMed
-
- Huang SY, Kim CY, Miller MJ, Gupta RT, Lessne ML, Horvath JJ, Boll DT, Evans PD, Befera NT, Krishnan P, Chan JL, Merkle EM. Abdominopelvic and lower extremity deep venous thrombosis: evaluation with contrast-enhanced MR venography with a blood-pool agent. Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201:208–214. - PubMed
-
- Pagnan L, Tona G, Belgrano M, Cova M, Pozzi Mucelli R. Direct contrast enhanced MR in the study of central venous accesses in children receiving total parenteral nutrition. Radiol Med. 2005;110:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Cowper SE, Robin HS, Steinberg SM, Su LD, Gupta S, LeBoit PE. Scleromyxoedema-like cutaneous diseases in renal-dialysis patients. Lancet. 2000;356:1000–1001. - PubMed
-
- Grobner T. Gadolinium–a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:1104–1108. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

