Genome resilience and prevalence of segmental duplications following fast neutron irradiation of soybean
- PMID: 25213171
- PMCID: PMC4224183
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.114.170340
Genome resilience and prevalence of segmental duplications following fast neutron irradiation of soybean
Abstract
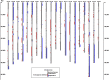
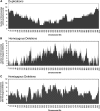
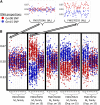
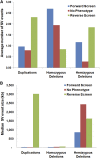
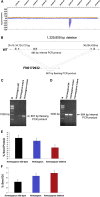
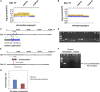
Fast neutron radiation has been used as a mutagen to develop extensive mutant collections. However, the genome-wide structural consequences of fast neutron radiation are not well understood. Here, we examine the genome-wide structural variants observed among 264 soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] plants sampled from a large fast neutron-mutagenized population. While deletion rates were similar to previous reports, surprisingly high rates of segmental duplication were also found throughout the genome. Duplication coverage extended across entire chromosomes and often prevailed at chromosome ends. High-throughput resequencing analysis of selected mutants resolved specific chromosomal events, including the rearrangement junctions for a large deletion, a tandem duplication, and a translocation. Genetic mapping associated a large deletion on chromosome 10 with a quantitative change in seed composition for one mutant. A tandem duplication event, located on chromosome 17 in a second mutant, was found to cosegregate with a short petiole mutant phenotype, and thus may serve as an example of a morphological change attributable to a DNA copy number gain. Overall, this study provides insight into the resilience of the soybean genome, the patterns of structural variation resulting from fast neutron mutagenesis, and the utility of fast neutron-irradiated mutants as a source of novel genetic losses and gains.
Keywords: deletion; duplication; fast neutron; soybean; structural variation.
Copyright © 2014 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fast neutron-induced structural rearrangements at a soybean NAP1 locus result in gnarled trichomes.Theor Appl Genet. 2016 Sep;129(9):1725-38. doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2735-x. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Theor Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 27282876 Free PMC article.
-
An Induced Chromosomal Translocation in Soybean Disrupts a KASI Ortholog and Is Associated with a High-Sucrose and Low-Oil Seed Phenotype.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Apr 3;7(4):1215-1223. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.038596. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28235823 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and genomic analyses of a fast neutron mutant population resource in soybean.Plant Physiol. 2011 May;156(1):240-53. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.170811. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21321255 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse genetics by fast neutron mutagenesis in higher plants.Funct Integr Genomics. 2002 Nov;2(6):254-8. doi: 10.1007/s10142-002-0076-0. Epub 2002 Sep 20. Funct Integr Genomics. 2002. PMID: 12444418 Review.
-
Human adaptation and evolution by segmental duplication.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Dec;41:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27584858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plant Genome Editing and the Relevance of Off-Target Changes.Plant Physiol. 2020 Aug;183(4):1453-1471. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.01194. Epub 2020 May 26. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32457089 Free PMC article.
-
A chromosome 16 deletion conferring a high sucrose phenotype in soybean.Theor Appl Genet. 2023 Apr 11;136(5):109. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04354-6. Theor Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 37039870
-
Genomic changes and biochemical alterations of seed protein and oil content in a subset of fast neutron induced soybean mutants.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Oct 12;19(1):420. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1981-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31604426 Free PMC article.
-
Screening populations for copy number variation using genotyping-by-sequencing: a proof of concept using soybean fast neutron mutants.BMC Genomics. 2019 Aug 6;20(1):634. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5998-1. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31387530 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison and Characterization of Phenotypic and Genomic Mutations Induced by a Carbon-Ion Beam and Gamma-ray Irradiation in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 16;24(10):8825. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108825. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J., 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 494–498. - PubMed
-
- Bruggemann E., Handwerger K., Essex C., Storz G., 1996. Analysis of fast neutron-generated mutants at the Arabidopsis thaliana HY4 locus. Plant J. 10: 755–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- SRA/SRP036841
- SRA/SRX467183
- SRA/SRX467185
- SRA/SRX467191
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

