The role of +TIPs in directional tip expansion
- PMID: 25213368
- PMCID: PMC4213288
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.12791
The role of +TIPs in directional tip expansion
Abstract
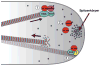
Aspergillus nidulans is an ideal model to study nuclear migration and intracellular transport by dynein and kinesin owing to its long neuron-like hyphae, conserved transport mechanisms, and powerful genetics. In this organism, as in other filamentous fungi, microtubules have been implicated in patterning cell shape through polarized tip growth - the hallmark mode of growth that generates the elongated hyphae. Exactly how microtubules regulate tip growth is incompletely understood and remains a fascinating question for various cell types, such as pollen tubes and root hairs. Zeng et al. (2014) describe important new findings in A. nidulans regarding the role of EBA, the master regulator of microtubule plus end-tracking proteins, in specifying microtubule dynamics required for directional tip growth at the hyphal tip.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Comment on
-
Microtubule plus end-tracking proteins play critical roles in directional growth of hyphae by regulating the dynamics of cytoplasmic microtubules in Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Nov;94(3):506-21. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12792. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25213466
Similar articles
-
Microtubule plus end-tracking proteins play critical roles in directional growth of hyphae by regulating the dynamics of cytoplasmic microtubules in Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Nov;94(3):506-21. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12792. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25213466
-
The role of microtubules in rapid hyphal tip growth of Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):918-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0798. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15548594 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus myosin-V supports polarized growth in the absence of microtubule-based transport.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028575. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194856 Free PMC article.
-
Interdependence of the actin and the microtubule cytoskeleton during fungal growth.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Aug;20:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 May 27. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24879477 Review.
-
Endocytosis and early endosome motility in filamentous fungi.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Aug;20:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 May 15. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24835422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of a vezatin-like protein for dynein-mediated early endosome transport.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Nov 1;26(21):3816-27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-08-0602. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26378255 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

