Immune dysregulation in human subjects with heterozygous germline mutations in CTLA4
- PMID: 25213377
- PMCID: PMC4371526
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1255904
Immune dysregulation in human subjects with heterozygous germline mutations in CTLA4
Abstract
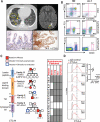
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is an inhibitory receptor found on immune cells. The consequences of mutations in CTLA4 in humans are unknown. We identified germline heterozygous mutations in CTLA4 in subjects with severe immune dysregulation from four unrelated families. Whereas Ctla4 heterozygous mice have no obvious phenotype, human CTLA4 haploinsufficiency caused dysregulation of FoxP3(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells, hyperactivation of effector T cells, and lymphocytic infiltration of target organs. Patients also exhibited progressive loss of circulating B cells, associated with an increase of predominantly autoreactive CD21(lo) B cells and accumulation of B cells in nonlymphoid organs. Inherited human CTLA4 haploinsufficiency demonstrates a critical quantitative role for CTLA-4 in governing T and B lymphocyte homeostasis.
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


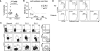
Comment in
-
Immunology. Autoimmunity by haploinsufficiency.Science. 2014 Sep 26;345(6204):1560-1. doi: 10.1126/science.1260791. Science. 2014. PMID: 25258064 No abstract available.
-
Balance and imbalance in the immune system: life on the edge.Immunity. 2014 Nov 20;41(5):682-4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Immunity. 2014. PMID: 25517610 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

