Mouse macrophages completely lacking Rho subfamily GTPases (RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC) have severe lamellipodial retraction defects, but robust chemotactic navigation and altered motility
- PMID: 25213860
- PMCID: PMC4215254
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.563270
Mouse macrophages completely lacking Rho subfamily GTPases (RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC) have severe lamellipodial retraction defects, but robust chemotactic navigation and altered motility
Abstract
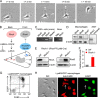
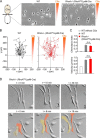
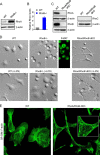
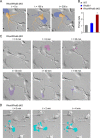
RhoA is thought to be essential for coordination of the membrane protrusions and retractions required for immune cell motility and directed migration. Whether the subfamily of Rho (Ras homolog) GTPases (RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC) is actually required for the directed migration of primary cells is difficult to predict. Macrophages isolated from myeloid-restricted RhoA/RhoB (conditional) double knock-out (dKO) mice did not express RhoC and were essentially "pan-Rho"-deficient. Using real-time chemotaxis assays, we found that retraction of the trailing edge was dissociated from the advance of the cell body in dKO cells, which developed extremely elongated tails. Surprisingly, velocity (of the cell body) was increased, whereas chemotactic efficiency was preserved, when compared with WT macrophages. Randomly migrating RhoA/RhoB dKO macrophages exhibited multiple small protrusions and developed large "branches" due to impaired lamellipodial retraction. A mouse model of peritonitis indicated that monocyte/macrophage recruitment was, surprisingly, more rapid in RhoA/RhoB dKO mice than in WT mice. In comparison with dKO cells, the phenotypes of single RhoA- or RhoB-deficient macrophages were mild due to mutual compensation. Furthermore, genetic deletion of RhoB partially reversed the motility defect of macrophages lacking the RhoGAP (Rho GTPase-activating protein) myosin IXb (Myo9b). In conclusion, the Rho subfamily is not required for "front end" functions (motility and chemotaxis), although both RhoA and RhoB are involved in pulling up the "back end" and resorbing lamellipodial membrane protrusions. Macrophages lacking Rho proteins migrate faster in vitro, which, in the case of the peritoneum, translates to more rapid in vivo monocyte/macrophage recruitment.
Keywords: Cell Migration; Cell Motility; Cell Polarity; Chemotaxis; Macrophage; Mouse; Myosin; Ras Homolog Gene Family, Member A (RhoA); Rho (Rho GTPase); Rho GTPases.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel strategy for specifically down-regulating individual Rho GTPase activity in tumor cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 7;278(45):44617-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308929200. Epub 2003 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12939257
-
XPLN, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for RhoA and RhoB, but not RhoC.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 8;277(45):42964-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207401200. Epub 2002 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12221096
-
The Role of RhoA, RhoB and RhoC GTPases in Cell Morphology, Proliferation and Migration in Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Infected Glioblastoma Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(1):94-109. doi: 10.1159/000438612. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26741994
-
A current overview of RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC functions in vascular biology and pathology.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;206:115321. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115321. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36306821 Review.
-
Why three Rho proteins? RhoA, RhoB, RhoC, and cell motility.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Nov 15;301(1):43-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.012. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15501444 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmodium berghei-Released Factor, PbTIP, Modulates the Host Innate Immune Responses.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 7;12:699887. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.699887. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34987497 Free PMC article.
-
E-cadherin loss in RMG-1 cells inhibits cell migration and its regulation by Rho GTPases.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019 May 14;18:100650. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.100650. eCollection 2019 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019. PMID: 31193165 Free PMC article.
-
The RhoB small GTPase in physiology and disease.Small GTPases. 2018 Sep 3;9(5):384-393. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1253528. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 27875099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cortactin deficiency causes increased RhoA/ROCK1-dependent actomyosin contractility, intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction, and disproportionately severe DSS-induced colitis.Mucosal Immunol. 2017 Sep;10(5):1237-1247. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.136. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Mucosal Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28120846
-
RhoA as a Key Regulator of Innate and Adaptive Immunity.Cells. 2019 Jul 17;8(7):733. doi: 10.3390/cells8070733. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31319592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ridley A. J., Schwartz M. A., Burridge K., Firtel R. A., Ginsberg M. H., Borisy G., Parsons J. T., Horwitz A. R. (2003) Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302, 1704–1709 - PubMed
-
- Abercrombie M., Heaysman J. E., Pegrum S. M. (1971) The locomotion of fibroblasts in culture. IV. Electron microscopy of the leading lamella. Exp. Cell Res. 67, 359–367 - PubMed
-
- Reig G., Pulgar E., Concha M. L. (2014) Cell migration: from tissue culture to embryos. Development 141, 1999–2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

