Epitope analysis of Ara h 2 and Ara h 6: characteristic patterns of IgE-binding fingerprints among individuals with similar clinical histories
- PMID: 25213872
- PMCID: PMC4470374
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.12407
Epitope analysis of Ara h 2 and Ara h 6: characteristic patterns of IgE-binding fingerprints among individuals with similar clinical histories
Abstract
Background: Ara h 2 and Ara h 6 are moderately homologous and highly potent peanut allergens.
Objective: To identify IgE-binding linear epitopes of Ara h 6, compare them to those of Ara h 2, and to stratify binding based on clinical histories.
Methods: Thirty highly peanut-allergic subjects were stratified by clinical history. Sera were diluted to contain the same amount of anti-peanut IgE. IgE binding to overlapping 20-mer peptides of Ara h 2 and Ara h 6 was assessed using microarrays.
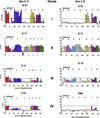
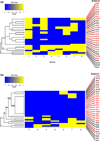
Results: Each subject had a unique IgE-binding fingerprint to peptides; these data were coalesced into epitope binding. IgE from subjects with a history of more severe reactions (n = 19) had a smaller frequency of binding events (BEs) for both Ara h 2 (52 BEs of 152 (19X8epitopes) possible BEs and Ara h 6 (13 BEs of 133 (19X7 epitopes) possible BEs) compared to IgE from those with milder histories (n = 11) (Ara h 2: 47 BEs of 88 (11X8 epitopes) possible BEs, P < 0.01; Ara h 6: 25 BEs of 77 (11X7 epitopes) possible BEs, P < 0.001). Using an unsupervised hierarchal cluster analysis, subjects with similar histories tended to cluster. We have tentatively identified a high-risk pattern of binding to peptides of Ara h 2 and Ara h 6, predominantly in subjects with a history of more severe reactions (OR = 12.6; 95% CI: 2.0-79.5; P < 0.01).
Conclusions and clinical relevance: IgE from patients with more severe clinical histories recognize fewer linear epitopes of Ara h 2 and Ara h 6 than do subjects with milder reactions and bind these epitopes in characteristic patterns. Close examination of IgE binding to epitopes of Ara h 2 and Ara h 6 may have prognostic value.
Keywords: Ara h 2; Ara h 6; IgE; allergens; microarrays; peanut; peptides.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Dreskin and Otsu have a patent pending based on methodology described in this manuscript. Dr. Guo does not have any conflict of interests to disclose regarding this manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Sicherer SH, Munoz-Furlong A, God-bold JH, Sampson HA. US prevalence of self-reported peanut, tree nut, and sesame allergy: 11-year follow-up. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Venter C, Arshad SH. Epidemiology of food allergy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2011;58:327–349. ix. - PubMed
-
- Sampson HA. Update on food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:805–819. quiz 820. - PubMed
-
- Wainstein BK, Yee A, Jelley D, Ziegler M, Ziegler JB. Combining skin prick, immediate skin application and spe-cific-IgE testing in the diagnosis of peanut allergy in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007;18:231–239. - PubMed
-
- Maloney JM, Rudengren M, Ahlstedt S, Bock SA, Sampson HA. The use of serum-specific IgE measurements for the diagnosis of peanut, tree nut, and seed allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:145–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

