CT angiographic features of symptom-producing plaque in moderate-grade carotid artery stenosis
- PMID: 25213881
- PMCID: PMC7965661
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A4098
CT angiographic features of symptom-producing plaque in moderate-grade carotid artery stenosis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Emerging evidence indicates that plaque imaging can improve stroke risk stratification in patients with carotid artery atherosclerosis. We studied the association between soft and hard (calcified) plaque thickness measurements on CTA and symptomatic disease status (ipsilateral stroke or TIA) in patients with moderate-grade carotid artery stenosis.
Materials and methods: We measured soft-plaque and hard-plaque thickness on CTA axial source images in each carotid artery plaque in subjects with NASCET 50%-69% ICA stenosis. We used logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic analyses to assess the strength of the association between thickness measurements and prior stroke or TIA.
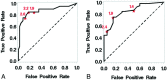
Results: Twenty of 72 vessels studied (27.7%) had ischemic symptoms ipsilateral to the side of moderate-grade carotid stenosis. Each 1-mm increase in soft plaque resulted in a 3.7 times greater odds of a prior ipsilateral ischemic event (95% CI, 1.9-7.2). Conversely, for each 1-mm increase in hard plaque, the odds of being symptomatic decreased by approximately 80% (OR, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.10%-0.48%). Receiver operating characteristic analysis showed an area under the curve of 0.88 by using soft-plaque thickness measurements to discriminate between asymptomatic and symptomatic plaques. Sensitivity and specificity were optimized by using a maximum soft-plaque thickness of 2.2 mm, which provided a sensitivity of 85% and a specificity of 83%.
Conclusions: Simple CTA plaque-thickness measurements might differentiate symptomatic and asymptomatic moderate-grade carotid artery plaque. With further prospective validation, CTA plaque measures could function as an easily implementable tool for risk stratification in carotid artery disease.
© 2015 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of Symptomatic Carotid Plaque Using Source Data from MR and CT Angiography: A Correlative Study.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;39(3-4):151-61. doi: 10.1159/000373918. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25721945 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of computed tomography angiography plaque thickness measurements in high-grade carotid artery stenosis.Stroke. 2014 Mar;45(3):740-5. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003882. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Stroke. 2014. PMID: 24496392
-
Optimal Carotid Plaque Features on Computed Tomography Angiography Associated With Ischemic Stroke.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Feb;10(5):e019462. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019462. Epub 2021 Feb 15. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33586471 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary carotid imaging: from degree of stenosis to plaque vulnerability.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan;124(1):27-42. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS142452. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26230478 Review.
-
Non-stenosing carotid artery plaques in embolic stroke of undetermined source: a retrospective analysis.Neurol Sci. 2023 Jan;44(1):247-252. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06425-w. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36166175 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of Symptomatic Carotid Plaque Using Source Data from MR and CT Angiography: A Correlative Study.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;39(3-4):151-61. doi: 10.1159/000373918. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25721945 Free PMC article.
-
Carotid artery plaque characterization with a wide-detector computed tomography using a dedicated post-processing 3D analysis: comparison with histology.Radiol Med. 2019 Sep;124(9):795-803. doi: 10.1007/s11547-019-01026-8. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Radiol Med. 2019. PMID: 30903605
-
Nonstenotic carotid artery plaques on computed tomography angiography in embolic stroke of undetermined source.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 20;103(51):e40880. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040880. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39705450 Free PMC article.
-
Nonstenotic carotid plaque on CT angiography in patients with cryptogenic stroke.Neurology. 2016 Aug 16;87(7):665-72. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002978. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27412144 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Correlation Between Distribution Location and Vulnerability of Carotid Plaque in Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2024 Mar 4;20:77-87. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S447418. eCollection 2024. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2024. PMID: 38464675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rothwell PM, Eliasziw M, Gutnikov SA, et al. . Analysis of pooled data from the randomised controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Lancet 2003;361:107–16 - PubMed
-
- Abbott AL. Medical (nonsurgical) intervention alone is now best for prevention of stroke associated with asymptomatic severe carotid stenosis: results of a systematic review and analysis. Stroke 2009;40:e573–83 - PubMed
-
- Raman G, Moorthy D, Hadar N, et al. . Management strategies for asymptomatic carotid stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2013;158:676–85 - PubMed
-
- Caplan LR, Hennerici M. Impaired clearance of emboli (washout) is an important link between hypoperfusion, embolism, and ischemic stroke. Arch Neurol 1998;55:1475–82 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
