Adiponectin is not required for exercise training-induced improvements in glucose and insulin tolerance in mice
- PMID: 25214523
- PMCID: PMC4270243
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12146
Adiponectin is not required for exercise training-induced improvements in glucose and insulin tolerance in mice
Abstract
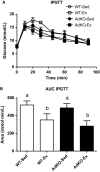
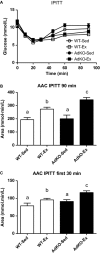
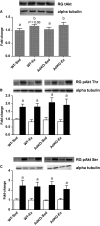
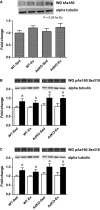
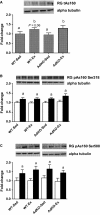
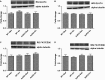
Adiponectin (Ad) is a potent insulin-sensitizing adipokine that has been found to activate pathways involved in the adaptation to exercise. Therefore, we examined whether Ad is required for the increased insulin response observed following exercise training in Ad knockout mice (AdKO). Eight weeks of exercise training significantly increased glucose and insulin tolerance in both wild type (WT) and AdKO mice. There were no differences in glucose tolerance between genotypes but insulin tolerance was improved to a greater extent in AdKO compared to WT mice following exercise training (+26%, P < 0.05). There were no genotype differences in the insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of AKT or AS160 in red or white gastrocnemius muscle (RG, WG). Exercise training increased total AKT and AS160 protein content in RG and total AS160 protein content in WG. There were no genotype differences in total AKT or AS160. However, exercise training induced a more robust increase in total AS160 in RG from AdKO (+44 ± 8%, P < 0.05) compared to WT mice (+28 ± 7%, P = 0.06). There were no differences in total GLUT4 or FAT/CD36 in RG or WG in WT or AdKO, with or without exercise training. Similarly, there were no differences in RER, VO2, or activity between any groups. Our results indicate the presence of Ad is not required for exercise-induced increases in insulin response. Furthermore, it appears that exercise may improve insulin sensitivity to a greater extent in the absence of Ad, suggesting the presence of an unknown compensatory mechanism.
Keywords: Adiponectin; adiponectin knockout mice; exercise training; glucose and insulin tolerance; insulin response; skeletal muscle.
© 2014 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Arita Y., Kihara S., Ouchi N., Takahashi M., Maeda K., Miyagawa J. 1999. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose‐specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.; 257:79-83. - PubMed
-
- Berg A. H., Combs T. P., Du X., Brownlee M., Scherer P. E. 2001. The adipocyte‐secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat. Med.; 7:947-953. - PubMed
-
- Bruce C. R., Anderson M. J., Carey A. L., Newman D. G., Bonen A., Kriketos A. D. 2003. Muscle oxidative capacity is a better predictor of insulin sensitivity than lipid status. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.; 88:5444-5451. - PubMed
-
- Bruce C. R., Mertz V. A., Heigenhauser G. J., Dyck D. J. 2005. The stimulatory effect of globular adiponectin on insulin‐stimulated glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation is impaired in skeletal muscle from obese subjects. Diabetes; 54:3154-3160. - PubMed
-
- Cartee G. D., Holloszy J. O. 1990. Exercise increases susceptibility of muscle glucose transport to activation by various stimuli. Am. J. Physiol.; 258:E390-E393. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

