Peroxisomal ubiquitin-protein ligases peroxin2 and peroxin10 have distinct but synergistic roles in matrix protein import and peroxin5 retrotranslocation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 25214533
- PMCID: PMC4226347
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.247148
Peroxisomal ubiquitin-protein ligases peroxin2 and peroxin10 have distinct but synergistic roles in matrix protein import and peroxin5 retrotranslocation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
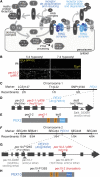
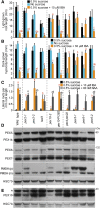
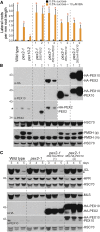
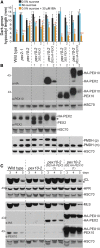
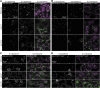
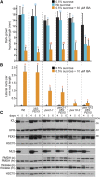
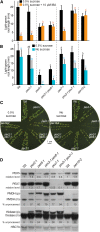
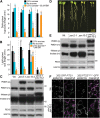
Peroxisomal matrix proteins carry peroxisomal targeting signals (PTSs), PTS1 or PTS2, and are imported into the organelle with the assistance of peroxin (PEX) proteins. From a microscopy-based screen to identify Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) mutants defective in matrix protein degradation, we isolated unique mutations in PEX2 and PEX10, which encode ubiquitin-protein ligases anchored in the peroxisomal membrane. In yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), PEX2, PEX10, and a third ligase, PEX12, ubiquitinate a peroxisome matrix protein receptor, PEX5, allowing the PEX1 and PEX6 ATP-hydrolyzing enzymes to retrotranslocate PEX5 out of the membrane after cargo delivery. We found that the pex2-1 and pex10-2 Arabidopsis mutants exhibited defects in peroxisomal physiology and matrix protein import. Moreover, the pex2-1 pex10-2 double mutant exhibited severely impaired growth and synergistic physiological defects, suggesting that PEX2 and PEX10 function cooperatively in the wild type. The pex2-1 lesion restored the unusually low PEX5 levels in the pex6-1 mutant, implicating PEX2 in PEX5 degradation when retrotranslocation is impaired. PEX5 overexpression altered pex10-2 but not pex2-1 defects, suggesting that PEX10 facilitates PEX5 retrotranslocation from the peroxisomal membrane. Although the pex2-1 pex10-2 double mutant displayed severe import defects of both PTS1 and PTS2 proteins into peroxisomes, both pex2-1 and pex10-2 single mutants exhibited clear import defects of PTS1 proteins but apparently normal PTS2 import. A similar PTS1-specific pattern was observed in the pex4-1 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme mutant. Our results indicate that Arabidopsis PEX2 and PEX10 cooperate to support import of matrix proteins into plant peroxisomes and suggest that some PTS2 import can still occur when PEX5 retrotranslocation is slowed.
© 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Agne B, Meindl NM, Niederhoff K, Einwächter H, Rehling P, Sickmann A, Meyer HE, Girzalsky W, Kunau WH. (2003) Pex8p: an intraperoxisomal organizer of the peroxisomal import machinery. Mol Cell 11: 635–646 - PubMed
-
- Azevedo JE, Schliebs W. (2006) Pex14p, more than just a docking protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763: 1574–1584 - PubMed
-
- Bartel B, Burkhart SE, Fleming WA. (2014a) Protein transport in and out of plant peroxisomes. In C Brocard, A Hartig, eds, Molecular Machines Involved in Peroxisome Biogenesis and Maintenance. Springer-Verlag, Vienna, pp 325–345
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

