Direct detection of ABCA1-dependent HDL formation based on lipidation-induced hydrophobicity change in apoA-I
- PMID: 25214539
- PMCID: PMC4617144
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D049445
Direct detection of ABCA1-dependent HDL formation based on lipidation-induced hydrophobicity change in apoA-I
Abstract
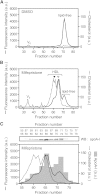
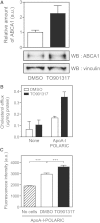
ABCA1 mediates the efflux of cholesterol and phospholipids into apoA-I to form HDL, which is important in the prevention of atherosclerosis. To develop a novel method for the evaluation of HDL formation, we prepared an apoA-I-POLARIC by labeling the specific residue of an apoA-I variant with a hydrophobicity-sensitive fluorescence probe that detects the environmental change around apoA-I during HDL formation. apoA-I-POLARIC possesses the intact ABCA1-dependent HDL formation activity and shows 4.0-fold higher fluorescence intensity in HDL particles than in the lipid-free state. Incubation of apoA-I-POLARIC with ABCA1-expressing cells, but not ABCA1-non-expressing cells, caused a 1.7-fold increase in fluorescence intensity. Gel filtration analysis demonstrated that the increase in fluorescence intensity of apoA-I-POLARIC represents the amount of apoA-I incorporated into the discoidal HDL particles rather than the amount of secreted cholesterol. THP-1 macrophage-mediated HDL formation and inhibition of HDL formation by cyclosporine A could also be measured using apoA-I-POLARIC. Furthermore, HDL formation-independent lipid release induced by microparticle formation or cell death was not detected by apoA-I-POLARIC. These results demonstrate that HDL formation by ABCA1-expressing cells can be specifically detected by sensing hydrophobicity change in apoA-I, thus providing a novel method for assessing HDL formation and screening of the HDL formation modulator.
Keywords: ATP binding cassette transporter A1; POLARIC; apolipoprotein A-I; cholesterol efflux; high density lipoprotein; hydrophobicity-sensitive fluorescence probe.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ATP binding cassette A1 (ABCA1) mediates microparticle formation during high-density lipoprotein (HDL) biogenesis.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Feb;257:90-99. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28129550
-
The roles of C-terminal helices of human apolipoprotein A-I in formation of high-density lipoprotein particles.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1841(1):80-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24120703 Free PMC article.
-
Current models of apolipoprotein A-I lipidation by adenosine triphosphate binding cassette transporter A1.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2022 Apr 1;33(2):139-145. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000786. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2022. PMID: 34581311 Review.
-
ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux generates microparticles in addition to HDL through processes governed by membrane rigidity.J Lipid Res. 2009 Mar;50(3):456-466. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800345-JLR200. Epub 2008 Oct 21. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 18941142
-
Role of apoA-I, ABCA1, LCAT, and SR-BI in the biogenesis of HDL.J Mol Med (Berl). 2006 Apr;84(4):276-94. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0030-4. Epub 2006 Feb 25. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16501936 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Phosphatidylserine and Cholesterol on Membrane-mediated Fibril Formation by the N-terminal Amyloidogenic Fragment of Apolipoprotein A-I.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 3;8(1):5497. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23920-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29615818 Free PMC article.
-
High density lipoproteins: Measurement techniques and potential biomarkers of cardiovascular risk.BBA Clin. 2015 Jan 31;3:175-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2015.01.005. eCollection 2015 Jun. BBA Clin. 2015. PMID: 26674734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunochemical Approach for Monitoring of Structural Transition of ApoA-I upon HDL Formation Using Novel Monoclonal Antibodies.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 7;7(1):2988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03208-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28592796 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular interaction and cytotoxicity of the iowa mutation of apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-IIowa) amyloid mediated by sulfate moieties of heparan sulfate.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 2;290(40):24210-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.652545. Epub 2015 Aug 19. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26292220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagao K., Kimura Y., Mastuo M., Ueda K. 2010. Lipid outward translocation by ABC proteins. FEBS Lett. 584: 2717–2723. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama S. 2006. Assembly of high-density lipoprotein. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 26: 20–27. - PubMed
-
- Nagao K., Tomioka M., Ueda K. 2011. Function and regulation of ABCA1–membrane meso-domain organization and reorganization. FEBS J. 278: 3190–3203. - PubMed
-
- Vedhachalam C., Duong P. T., Nickel M., Nguyen D., Dhanasekaran P., Saito H., Rothblat G. H., Lund-Katz S., Phillips M. C. 2007. Mechanism of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-mediated cellular lipid efflux to apolipoprotein A-I and formation of high density lipoprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem. 282: 25123–25130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

