Innate lymphoid cells regulate intestinal epithelial cell glycosylation
- PMID: 25214634
- PMCID: PMC4774895
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1254009
Innate lymphoid cells regulate intestinal epithelial cell glycosylation
Abstract
Fucosylation of intestinal epithelial cells, catalyzed by fucosyltransferase 2 (Fut2), is a major glycosylation mechanism of host-microbiota symbiosis. Commensal bacteria induce epithelial fucosylation, and epithelial fucose is used as a dietary carbohydrate by many of these bacteria. However, the molecular and cellular mechanisms that regulate the induction of epithelial fucosylation are unknown. Here, we show that type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) induced intestinal epithelial Fut2 expression and fucosylation in mice. This induction required the cytokines interleukin-22 and lymphotoxin in a commensal bacteria-dependent and -independent manner, respectively. Disruption of intestinal fucosylation led to increased susceptibility to infection by Salmonella typhimurium. Our data reveal a role for ILC3 in shaping the gut microenvironment through the regulation of epithelial glycosylation.
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
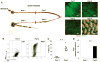
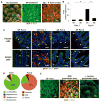
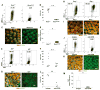
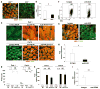
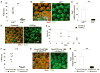
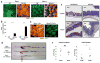
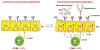
Comment in
-
Immunology. Innate lymphoid cells sweeten the pot.Science. 2014 Sep 12;345(6202):1248-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1259808. Science. 2014. PMID: 25214594 No abstract available.
-
Tolerance: AIREs and graces.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Nov;14(11):714-5. doi: 10.1038/nri3762. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25324122 No abstract available.
-
Microbiota: support your friends to resist your enemies.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Nov;14(11):715. doi: 10.1038/nri3765. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25341430 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

