Shaking up the system: the role of change in maternal-adolescent communication quality and adolescent weight loss
- PMID: 25214645
- PMCID: PMC4288305
- DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsu073
Shaking up the system: the role of change in maternal-adolescent communication quality and adolescent weight loss
Abstract
Objective: The association between directly observed mother-adolescent weight-related communication quality and adolescent percent overweight within the context of an adolescent weight control study was examined.
Methods: As part of a larger study examining the impact of a behavioral weight control intervention that included attention to parent-adolescent communication (Standard Behavioral Treatment + Enhanced Parenting, SBT + EP) compared with an efficacious Standard Behavioral Treatment (SBT), 38 mother-adolescent dyads participated in a weight-related videotaped discussion. Discussions were taped and collected pre- and postintervention.
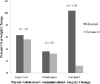
Results: No significant differences emerged in the quality of mother-adolescent communication between SBT (n = 19) and SBT + EP (n = 19) participants, nor was baseline mother-adolescent communication quality associated with adolescents' weight loss in either condition. However, a decline in communication quality was associated with better outcomes for adolescents participating in the SBT group.
Conclusions: This study provides preliminary evidence that a change in mother-adolescent communication is associated with successful weight loss among adolescents.
Keywords: adolescents; parent-adolescent communication; weight management.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Pediatric Psychology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Ackard D M, Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M, Perry C. Parent–child connectedness and behavioral and emotional health among adolescents. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2006;30:59–66. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury T, Fincham F. Attributions in marriage: Review and critique. Psychological Bulletin. 1990;107:3–33. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.107.1.3. - PubMed
-
- Brownell K D, Kelman J H, Stunkard A J. Treatment of obese children with and without their mothers: Changes in weight and blood pressure. Pediatrics. 1983;71:515–523. - PubMed
-
- Christensen A, Margolin G, editors. Conflict and alliance in distressed and nondistressed families. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

