Combining structure-based pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, and in silico ADMET analysis to discover novel tetrahydro-quinoline based pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 activators with antitumor activity
- PMID: 25214764
- PMCID: PMC4159224
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S62921
Combining structure-based pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, and in silico ADMET analysis to discover novel tetrahydro-quinoline based pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 activators with antitumor activity
Abstract
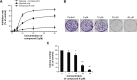
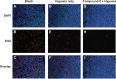
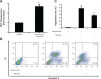
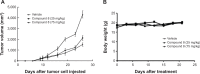
Compared with normal differentiated cells, cancer cells upregulate the expression of pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 (PKM2) to support glycolytic intermediates for anabolic processes, including the synthesis of nucleic acids, amino acids, and lipids. In this study, a combination of the structure-based pharmacophore modeling and a hybrid protocol of virtual screening methods comprised of pharmacophore model-based virtual screening, docking-based virtual screening, and in silico ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity) analysis were used to retrieve novel PKM2 activators from commercially available chemical databases. Tetrahydroquinoline derivatives were identified as potential scaffolds of PKM2 activators. Thus, the hybrid virtual screening approach was applied to screen the focused tetrahydroquinoline derivatives embedded in the ZINC database. Six hit compounds were selected from the final hits and experimental studies were then performed. Compound 8 displayed a potent inhibitory effect on human lung cancer cells. Following treatment with Compound 8, cell viability, apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production were examined in A549 cells. Finally, we evaluated the effects of Compound 8 on mice xenograft tumor models in vivo. These results may provide important information for further research on novel PKM2 activators as antitumor agents.
Keywords: molecular docking; pharmacophore; pyruvate kinase; virtual screening.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery and structure-activity relationship of novel 4-hydroxy-thiazolidine-2-thione derivatives as tumor cell specific pyruvate kinase M2 activators.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:48-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.023. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29172082
-
Discovery of boronic acid-based potent activators of tumor pyruvate kinase M2 and development of gastroretentive nanoformulation for oral dosing.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Jun 15;42:128062. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128062. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 33901643
-
Synthesis of novel 7-azaindole derivatives containing pyridin-3-ylmethyl dithiocarbamate moiety as potent PKM2 activators and PKM2 nucleus translocation inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 15;170:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30878825
-
Activators of PKM2 in cancer metabolism.Future Med Chem. 2014 Jun;6(10):1167-78. doi: 10.4155/fmc.14.70. Future Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25078136 Review.
-
Pyruvate kinase activators as a therapy target: a patent review 2011-2017.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Jan;28(1):61-68. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2018.1391218. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018. PMID: 28994333 Review.
Cited by
-
An allostatic mechanism for M2 pyruvate kinase as an amino-acid sensor.Biochem J. 2018 May 31;475(10):1821-1837. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180171. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29748232 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand and Structure-Based Virtual Screening in Combination, to Evaluate Small Organic Molecules as Inhibitors for the XIAP Anti-Apoptotic Protein: The Xanthohumol Hypothesis.Molecules. 2022 Jul 28;27(15):4825. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154825. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956774 Free PMC article.
-
Base-Promoted Synthesis of β-Substituted-Tryptophans via a Simple and Convenient Three-Component Condensation of Nickel(II) Glycinate.Molecules. 2017 Apr 27;22(5):695. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050695. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28448432 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Deep Learning Based Method for Molecular Similarity Searching Using Stack of Deep Belief Networks.Molecules. 2020 Dec 29;26(1):128. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010128. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33383976 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel potential selective HDAC8 inhibitors by combine ligand-based, structure-based virtual screening and in-vitro biological evaluation.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 20;9(1):17174. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53376-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31748509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Wu N, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Nature. 2008;452:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Chaneton B, Gottlieb E. Rocking cell metabolism: revised functions of the key glycolytic regulator PKM2 in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012;37:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 2008;452:230–233. - PubMed
-
- Altenberg B, Greulich KO. Genes of glycolysis are ubiquitously overexpressed in 24 cancer classes. Genomics. 2004;84:1014–1020. - PubMed
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

