Reducing the burden of regular indwelling urinary catheter changes in the catheter clinics: the opinion of patients and relatives on the practice of self-catheterization
- PMID: 25214771
- PMCID: PMC4159498
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S66520
Reducing the burden of regular indwelling urinary catheter changes in the catheter clinics: the opinion of patients and relatives on the practice of self-catheterization
Abstract
Background: Clean intermittent self-catheterization is accepted worldwide as a standard of care for patients with long-standing need for urinary bladder decompression. Evidence of its routine practice in our low-resource setting is lacking, leading to increasing number of patients with a long-standing indwelling urinary catheter.
Objective: To seek the opinion of patients already using indwelling catheters regarding the practice of self-catheterization.
Patients and methods: Over a 4-month period, the opinion of every patient and patient's relative that attended the regular urinary catheter clinic was sought using an intern-administered questionnaire. The data was analyzed using SPSS version 20.
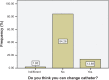
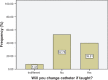
Results: A total of 108 patients completed the questionnaire. Age range was 16-100 years with a mean of 62.2±15.5 years. Only 30.5% of the patients had formal education beyond the primary level. The median cost for change of the indwelling catheter was 1,325 naira ($8.28 US) with a range of 500-4,000 naira ($3.13-$25 USD). Analysis showed that: 70.8% of patients aged under 60 years/60.6% of those with formal education beyond primary level/61.9% of those wearing catheters for <3 months would give consent for training in self-catheterization. Higher cost of catheter change did not influence the decision to consider self-catheterization. Of the 59 patient relatives who completed the questionnaire, 63% of those younger than 50 years old and 69.2% of those with tertiary education would be willing to undertake training to administer self-catheterization.
Conclusion: A select group of patients and accompanying relatives in our low-resource setting are willing to learn and practice self-catheterization.
Keywords: indwelling catheter; patients’ opinion; self-catheterization.
Figures
References
-
- Di Benedetto P. Clean intermittent self-catheterization in neuro-urology. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2011;47(4):651–659. - PubMed
-
- Le Breton F, Guinet A, Verollet D, Jousse M, Amarenco G. Therapeutic education and intermittent self-catheterization: recommendations for an educational program and a literature review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;55(3):201–212. - PubMed
-
- Cochran S. Care of the indwelling urinary catheter: is it evidence based? J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2007;34(3):282–288. - PubMed
-
- van Achterberg T, Holleman G, Cobussen-Boekhorst H, Arts R, Heesakkers J. Adherence to clean intermittent self-catheterization procedures: determinants explored. J Clin Nurs. 2008;17(3):394–402. - PubMed
-
- Wyndaele JJ. Complications of intermittent catheterization: their prevention and treatment. Spinal Cord. 2002;40(10):536–541. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources