In vitro evaluation of endothelial exosomes as carriers for small interfering ribonucleic acid delivery
- PMID: 25214786
- PMCID: PMC4159392
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S64267
In vitro evaluation of endothelial exosomes as carriers for small interfering ribonucleic acid delivery
Abstract
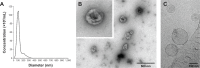
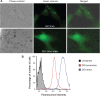
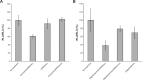
Exosomes, one subpopulation of nanosize extracellular vesicles derived from multivesicular bodies, ranging from 30 to 150 nm in size, emerged as promising carriers for small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) delivery, as they are capable of transmitting molecular messages between cells through carried small noncoding RNAs, messenger RNAs, deoxyribonucleic acids, and proteins. Endothelial cells are involved in a number of important biological processes, and are a major source of circulating exosomes. In this study, we prepared exosomes from endothelial cells and evaluated their capacity to deliver siRNA into primary endothelial cells. Exosomes were isolated and purified by sequential centrifugation and ultracentrifugation from cultured mouse aortic endothelial cells. Similar to exosome particles from other cell sources, endothelial exosomes are nanometer-size vesicles, examined by both the NanoSight instrument and transmission electron microscopy. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis confirmed the expression of two exosome markers: CD9 and CD63. Flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy studies demonstrated that endothelial exosomes were heterogeneously distributed within cells. In a gene-silencing study with luciferase-expressing endothelial cells, exosomes loaded with siRNA inhibited luciferase expression by more than 40%. In contrast, siRNA alone and control siRNA only suppressed luciferase expression by less than 15%. In conclusion, we demonstrated that endothelial exosomes have the capability to accommodate and deliver short foreign nucleic acids into endothelial cells.
Keywords: endothelium; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; gene delivery; siRNA.
Figures
References
-
- Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–659. - PubMed
-
- Denzer K, Kleijmeer MJ, Heijnen HF, Stoorvogel W, Geuze HJ. Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 19):3365–3374. - PubMed
-
- Loyer X, Vion AC, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM. Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 2014;114(2):345–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

