Autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine regulates the expression of LC3, Beclin-1 and ZnTs in rat cerebral cortex following recurrent neonatal seizures
- PMID: 25214972
- PMCID: PMC4129681
Autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine regulates the expression of LC3, Beclin-1 and ZnTs in rat cerebral cortex following recurrent neonatal seizures
Abstract
Background: Autophagy is a homeostatic process for intracellular recycling of bulk proteins and aging organelles. Increased autophagy has now been reported in experimental models of traumatic brain injury, stroke and excitotoxicity, and in patients with Alzheimer's disease and critical illness. The role of autophagy in developmental epilepsy, however, is unknown. The present study was to investigate the effects of recurrent neonatal seizure, in the presence and absence of autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA), on the acute phase gene expression of ZnTs, LC3 and Beclin-1 in rat cerebral cortex and the interaction among them.
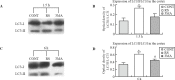
Methods: Thirty-six Sprague-Dawley neonatal rats at postnatal day 6(P6) were randomly divided into three groups: a recurrent-seizures group (RS, n=12), a 3-MA treated-seizure group (3-MA group, each rat pretreated with 3-methyladenine before seizures, 100nmol/μl/day, i.p., n=12) and a control group (n=12). At 1.5 and 6 hours after the last seizures, the mRNA levels of ZnT1-ZnT3, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B light chain 3 (LC3) and beclin-1 were detected using the real-time RT-PCR method. The LC3 protein level was examined by Western blotting.
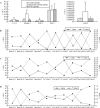
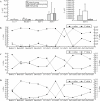
Results: The levels of LC3, beclin-1 and ZnT-2 transcripts in the RS group elevated significantly at 1.5 and 6 hours after the last seizures compared with those in the control and 3-MA groups. At the interval of 1.5 hours, the mRNA level of ZnT-1 increased significantly after the last seizure compared with that in the control group. There was no significant difference in the transcript levels of ZnT-3 among the three groups. Linear correlation analysis showed that the expression of the five genes in the control group exhibited a significant inter-relationship. In the 3-MA group, however, the inter-relationship was only found between beclin-1 and ZnT-1. In the RS group, the inter-relationship was not observed.
Conclusions: The autophagy/lysosomal pathway is immediately activated along with the elevated expression of ZnT1 and ZnT2 in the cerebral cortex after recurrent seizures. 3-MA is involved in the regulation of the autophagy/lysosomal pathway and ZnTs by down-regulating the expression of LC3 and beclin-1.
Keywords: Beclin-1; LC3; Seizure; Zinc transporter 1; Zinc transporter 3.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute phase expression pattern of ZnTs, LC3, and beclin-1 in rat Hippocampus and its regulation by 3-methyladenine following recurrent neonatal seizures.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011 Oct;143(1):320-31. doi: 10.1007/s12011-010-8836-5. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011. PMID: 20838925
-
Dynamic pattern of gene expression of ZnT-4, caspase-3, LC3, and PRG-3 in rat cerebral cortex following flurothyl-induced recurrent neonatal seizures.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011 Dec;143(3):1607-15. doi: 10.1007/s12011-011-8982-4. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011. PMID: 21286846
-
Leptin-regulated autophagy plays a role in long-term neurobehavioral injury after neonatal seizures and the regulation of zinc/cPLA2 and CaMK II signaling in cerebral cortex.Epilepsy Res. 2018 Oct;146:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2018.07.023. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Epilepsy Res. 2018. PMID: 30092488
-
Dynamic pattern of gene expression of ZnT-1, ZnT-3 and PRG-1 in rat brain following flurothyl-induced recurrent neonatal seizures.Toxicol Lett. 2010 May 4;194(3):86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.02.008. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Toxicol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20167268
-
Protective effects of autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine on ischemia-reperfusion-induced retinal injury.Int Ophthalmol. 2020 May;40(5):1095-1101. doi: 10.1007/s10792-019-01272-9. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Int Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31916058
Cited by
-
Human retinal pigment epithelial cells are protected against hypoxia by BNIP3.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Nov;8(22):1502. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-7145. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33313247 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Endothelial Dysfunction and Autophagy in Fibromyalgia-Related Vascular and Cerebral Cortical Changes and the Ameliorative Effect of Fisetin.Cells. 2021 Dec 24;11(1):48. doi: 10.3390/cells11010048. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011610 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy in Refractory Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients with Hippocampal Sclerosis.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;38(2):479-486. doi: 10.1007/s10571-017-0492-2. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28405902 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory effects of clomiphene and tamoxifen on mTOR and LC3-II expressions in relation to autophagy in experimental polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Mar;49(3):1721-1729. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06981-y. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34813001
-
Salidroside protects cortical neurons against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity by inhibiting autophagy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;419(1-2):53-64. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2749-3. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27357827
References
-
- Ben-Ari Y, Holmes GL. Effects of seizures on developmental processes in the immature brain. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:1055–1063. - PubMed
-
- Holmes GL. Effects of seizures on brain development: lessons from the laboratory. Pediatr Neurol. 2005;33:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Holopainen IE. Seizures in the developing brain: cellular and molecular mechanisms of neuronal damage, neurogenesis and cellular reorganization. Neurochem Int. 2008;52:935–947. - PubMed
-
- Missuya K, Nitta N, Suzuki F. Persistent zinc depletion in the mossy fiber terminals in the intrahippocampal kainite mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2009;50:1979–1990. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima AS, Dyck RH. Zinc and cortical plasticity. Brain. Res Rev. 2009;59:347–373. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
