Effect of ulinastatin on paraquat-induced-oxidative stress in human type II alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 25215107
- PMCID: PMC4129841
- DOI: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2013.02.009
Effect of ulinastatin on paraquat-induced-oxidative stress in human type II alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Ulinastatin (UTI) is a urinary trypsin inhibitor extracted and purified from urine of males. This study aimed to explore the effects of UTI on paraquat-induced-oxidative stress in human type II alveolar epithelial cells.
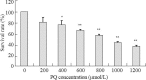
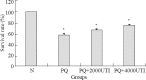
Methods: The human type II alveolar epithelial cells, A549 cells, were cultured in vitro. The A549 cells were treated with different concentrations of paraquat (200, 400, 600, 800, 1 000, 1 200 µmol/L) and ulinastatin(0, 2 000, 4 000, 6 000, 8 000 U/mL) for 24 hours, the cell viability was measured by cell counting kit-8 and the median lethal concentration was selected. In order to establish an in vitro model of paraquat intoxication and to determine the safe dose of ulinastatin, we calculated LD50 using cell counting kit-8 to determine the survival rate of the cells. A549 cells were divided into normal control group, paraquat group and paraquat+ulinastatin group. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) were detected by biochemistry colorimetry, while the level of reactive oxygen spies (ROS) was detected by DCFH-DA assay.
Results: The survival rate of A549 cells treated with different concentrations of paraquat decreased in a concentration-dependent manner. Whereas there was no decrease in the survival rate of cells treated with 0-4 000 U/mL ulinastatin. The levels of MDA, MPO, and ROS were significantly higher in the paraquat group than in the normal control group after 24-hour-exposure. And the survival rate of the paraquat+ulinastatin group was higher than that of the paraquat group, but lower than that of the normal control group. The levels of MDA, MPO, and ROS were lower than those of the paraquat group.
Conclusion: Ulinastatin can alleviate the paraquat-induced A549 cell damage by reducing oxidative stress.
Keywords: A549 cell; Oxidative stress; Paraquat; Ulinastatin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The protective effect of ulinastatin on paraquat-induced injury in HK-2 cells and the underlying mechanisms].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2015 Jul;33(7):501-6. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26653645 Chinese.
-
Edaravone attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress in human type II alveolar epithelial cells.World J Emerg Med. 2012;3(1):55-9. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2012.01.010. World J Emerg Med. 2012. PMID: 25215040 Free PMC article.
-
The ultra-early protective effect of ulinastatin on rabbit acute lung injury induced by paraquat.BMC Emerg Med. 2013;13 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S7. doi: 10.1186/1471-227X-13-S1-S7. Epub 2013 Jul 4. BMC Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 23902632 Free PMC article.
-
[Curcumin reduces paraquat-induced oxidative injury in A549 cells by activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Jan;32(1):44-9. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24428990 Chinese.
-
[The Role of TSP-1-CD47 in ROS-mediated Pulmonary Fibrosis Induced by Paraquat].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2018 Sep 20;36(9):653-661. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2018.09.003. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30419666 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Aqueous Thunbergia laurifolia leaf extract alleviates paraquat-induced lung injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Mar 22;22(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03567-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35317802 Free PMC article.
-
Total ginsenosides synergize with ulinastatin against septic acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):7385-90. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261640 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of SP-A/B in lipoic acid on acute paraquat poisoning.World J Emerg Med. 2014;5(1):57-62. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.01.010. World J Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 25215149 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the effects of paraquat-induced pulmonary injury in rats using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS-based metabonomics.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 May 31;12(3):527-538. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad040. eCollection 2023 Jun. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37397915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee SK, Ameno K, In SW, Yang JY, Kim KU, Koo KS, et al. Levels of paraquat in fatal intoxications. Int J Legal Med. 1999;112:198–200. - PubMed
-
- Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Chen KH, Huang WH, Hsu CW, Hsu HH, et al. Improved survival in severe paraquat poisoning with repeated pulse therapy of cyclophosphamide and steroids. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37:1006–1013. - PubMed
-
- Tong F, Liu FR, Zhang JJ. The study on expression of TNF-α in acute lung injury caused by paraquat arid the protection effect of rhubarb. Chin J Emerg Med. 2009;3:241–246.
-
- Wang RL, Tang X, Wu X, Xu R, Yu KL, Xu K. The relationship between HIF-1α expression and the early lung fibrosis in rats with acute paraquat poisoning. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2012;30:273–277. - PubMed
-
- Faner R, Rojas M, Macnee W, Agustí A. Abnormal lung aging in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:306–313. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
