Diabetic kidney disease: from epidemiology to clinical perspectives
- PMID: 25215271
- PMCID: PMC4160578
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2014.38.4.252
Diabetic kidney disease: from epidemiology to clinical perspectives
Abstract
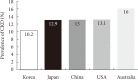
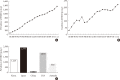
With worldwide epidemic of diabetes mellitus, diabetic nephropathy which is one of the major causes of microvascular complication has become a serious concern in Korea as well as the rest of the world. In view of its significance, there is an urgent and paramount need for proper managements that could either deter or slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Despite advances in care, ever increasing number of patients suffering from diabetic kidney disease and from end-stage renal disease implies that the current management is not adequate in many aspects. The reasons for these inadequacies compromise lack of early diagnosis, failure to intervene with timely and aggressive manner, and lack of understanding on the kind of interventions required. Another issue equally important for the adequate care of patients with diabetic nephropathy is an understanding of past, present and future epidemiology of diabetic nephropathy which serves, especially in Korea, as a material determining standard diagnosis and treatment and a national health-policy decision.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disorder; Diabetic nephropathies; Renal insufficiency, chronic; Renal replacement therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Hunsicker LG. The consequences and costs of chronic kidney disease before ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1363–1364. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Murray AM, Li S, Herzog CA, McBean AM, Eggers PW, Collins AJ. Chronic kidney disease and the risk for cardiovascular disease, renal replacement, and death in the United States Medicare population, 1998 to 1999. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Madan P, Kalra OP, Agarwal S, Tandon OP. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:440–444. - PubMed
-
- Chin HJ, Song YR, Lee JJ, Lee SB, Kim KW, Na KY, Kim S, Chae DW. Moderately decreased renal function negatively affects the health-related quality of life among the elderly Korean population: a population-based study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:2810–2817. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

