Aaptamines from the marine sponge Aaptos sp. display anticancer activities in human cancer cell lines and modulate AP-1-, NF-κB-, and p53-dependent transcriptional activity in mouse JB6 Cl41 cells
- PMID: 25215281
- PMCID: PMC4158141
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/469309
Aaptamines from the marine sponge Aaptos sp. display anticancer activities in human cancer cell lines and modulate AP-1-, NF-κB-, and p53-dependent transcriptional activity in mouse JB6 Cl41 cells
Abstract
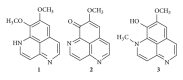
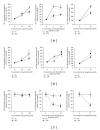
Aaptamine (8,9-dimethoxy-1H-benzo[de][1,6]naphthyridine) is a marine natural compound possessing antioxidative, antimicrobial, antifungal, and antiretroviral activity. Earlier, we have found that aaptamine and its derivatives demonstrate equal anticancer effects against the human germ cell cancer cell lines NT2 and NT2-R and cause some changes in the proteome of these cells. In order to explore further the mechanism of action of aaptamine and its derivatives, we studied the effects of aaptamine (1), demethyl(oxy)aaptamine (2), and isoaaptamine (3) on human cancer cell lines and on AP-1-, NF-κB-, and p53-dependent transcriptional activity in murine JB6 Cl41 cells. We showed that compounds 1-3 demonstrate anticancer activity in THP-1, HeLa, SNU-C4, SK-MEL-28, and MDA-MB-231 human cancer cell lines. Additionally, all compounds were found to prevent EGF-induced neoplastic transformation of murine JB6 Cl41 cells. Nuclear factors AP-1, NF-κB, and p53 are involved in the cellular response to high and nontoxic concentrations of aaptamine alkaloids 1-3. Furthermore, inhibition of EGF-induced JB6 cell transformation, which is exerted by the compounds 1-3 at low nontoxic concentrations of 0.7-2.1 μM, cannot be explained by activation of AP-1 and NF-κB.
Figures
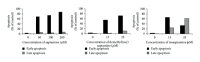
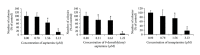
Similar articles
-
Four new aaptamine alkaloids from marine sponge Aaptos aaptos.Nat Prod Res. 2022 Oct;36(19):5022-5031. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.1917572. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Nat Prod Res. 2022. PMID: 33908314
-
Three new aaptamines from the marine sponge Aaptos sp. and their proapoptotic properties.Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Dec;5(12):1881-4. Nat Prod Commun. 2010. PMID: 21299112
-
Suberitine A-D, four new cytotoxic dimeric aaptamine alkaloids from the marine sponge Aaptos suberitoides.Org Lett. 2012 Apr 20;14(8):1994-7. doi: 10.1021/ol3004589. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Org Lett. 2012. PMID: 22472093
-
Review on marine sponge alkaloid, aaptamine: A potential antibacterial and anticancer drug.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022 Jan;99(1):103-110. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13932. Epub 2021 Aug 22. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 34331335 Review.
-
The role of AP-1, NF-kappaB and ROS/NOS in skin carcinogenesis: the JB6 model is predictive.Mol Cell Biochem. 2002 May-Jun;234-235(1-2):185-93. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12162432 Review.
Cited by
-
Inspired by Sea Urchins: Warburg Effect Mediated Selectivity of Novel Synthetic Non-Glycoside 1,4-Naphthoquinone-6S-Glucose Conjugates in Prostate Cancer.Mar Drugs. 2020 May 11;18(5):251. doi: 10.3390/md18050251. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32403427 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Activity of Naturally Derived Naphthyridines.Molecules. 2021 Jul 16;26(14):4324. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144324. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Citrinin Derivative from the Indonesian Marine Sponge-Associated Fungus Penicillium citrinum.Mar Drugs. 2020 Apr 24;18(4):227. doi: 10.3390/md18040227. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32344725 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Marine Fungal Asterripeptides A-C on In Vitro and In Vivo Staphylococcus aureus Skin Infection.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 8;17(10):1345. doi: 10.3390/ph17101345. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458986 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal Potential of Marine Organisms of the Yucatan Peninsula (Mexico) against Medically Important Candida spp.Molecules. 2023 Jan 6;28(2):606. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020606. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Larghi EL, Bohn ML, Kaufman TS. Aaptamine and related products. Their isolation, chemical syntheses, and biological activity. Tetrahedron. 2009;65(22):4257–4282.
-
- Aoki S, Kong D, Suna H, et al. Aaptamine, a spongean alkaloid, activates p21 promoter in a p53-independent manner. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2006;342(1):101–106. - PubMed
-
- Dyshlovoy SA, Naeth I, Venz S, et al. Proteomic profiling of germ cell cancer cells treated with aaptamine, a marine alkaloid with antiproliferative activity. Journal of Proteome Research. 2012;11(4):2316–2330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

