Cell-state-specific metabolic dependency in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis
- PMID: 25215489
- PMCID: PMC4197056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.048
Cell-state-specific metabolic dependency in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis
Abstract
The balance between oxidative and nonoxidative glucose metabolism is essential for a number of pathophysiological processes. By deleting enzymes that affect aerobic glycolysis with different potencies, we examine how modulating glucose metabolism specifically affects hematopoietic and leukemic cell populations. We find that a deficiency in the M2 pyruvate kinase isoform (PKM2) reduces the levels of metabolic intermediates important for biosynthesis and impairs progenitor function without perturbing hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), whereas lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) deletion significantly inhibits the function of both HSCs and progenitors during hematopoiesis. In contrast, leukemia initiation by transforming alleles putatively affecting either HSCs or progenitors is inhibited in the absence of either PKM2 or LDHA, indicating that the cell-state-specific responses to metabolic manipulation in hematopoiesis do not apply to the setting of leukemia. This finding suggests that fine-tuning the level of glycolysis may be explored therapeutically for treating leukemia while preserving HSC function.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

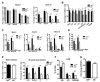

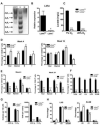
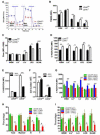
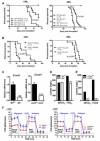
Comment in
-
Leukaemia: fine-tuning metabolism.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Nov;14(11):705. doi: 10.1038/nrc3839. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25291292 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M, Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993;7:812–821. - PubMed
-
- Behringer B, Pitako JA, Kunzmann R, Schmoor C, Behringer D, Mertelsmann R, Lubbert M. Prognosis of older patients with acute myeloid leukemia receiving either induction or noncurative treatment: a single-center retrospective study. Ann Hematol. 2003;82:381–389. - PubMed
-
- Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:85–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA163191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007287/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL044851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- C06 CA059267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA148180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA168653/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA147882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050234/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL044851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL087735/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL87735-4/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168653/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA147882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK050234/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

