A systematic analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters in the human microbiome reveals a common family of antibiotics
- PMID: 25215495
- PMCID: PMC4164201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.032
A systematic analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters in the human microbiome reveals a common family of antibiotics
Abstract
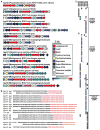
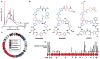
In complex biological systems, small molecules often mediate microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions. Using a systematic approach, we identified 3,118 small-molecule biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) in genomes of human-associated bacteria and studied their representation in 752 metagenomic samples from the NIH Human Microbiome Project. Remarkably, we discovered that BGCs for a class of antibiotics in clinical trials, thiopeptides, are widely distributed in genomes and metagenomes of the human microbiota. We purified and solved the structure of a thiopeptide antibiotic, lactocillin, from a prominent member of the vaginal microbiota. We demonstrate that lactocillin has potent antibacterial activity against a range of Gram-positive vaginal pathogens, and we show that lactocillin and other thiopeptide BGCs are expressed in vivo by analyzing human metatranscriptomic sequencing data. Our findings illustrate the widespread distribution of small-molecule-encoding BGCs in the human microbiome, and they demonstrate the bacterial production of drug-like molecules in humans. PAPERCLIP:
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Microbiome: Commensally sourced antibiotics.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014 Nov;12(11):726. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3363. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25244083 No abstract available.
-
Antimicrobials: Commensally sourced antibiotics.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Nov;13(11):812. doi: 10.1038/nrd4474. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25359376 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baumann H, Tzianabos AO, Brisson JR, Kasper DL, Jennings HJ. Structural elucidation of two capsular polysaccharides from one strain of Bacteroides fragilis using high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992;31:4081–4089. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

