Diltiazem reduces mortality and breakdown of ATP in red blood cell induced by isoproterenol in a freely moving rat model in vivo
- PMID: 25215514
- PMCID: PMC4192692
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo4030775
Diltiazem reduces mortality and breakdown of ATP in red blood cell induced by isoproterenol in a freely moving rat model in vivo
Abstract
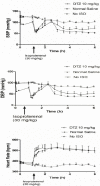
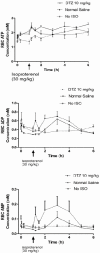
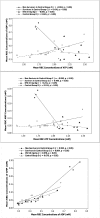
The benefit of calcium channel blockers for cardiovascular prevention against heart attack and stroke has not been firmly supported. We investigated the possible cardiovascular protective effect of diltiazem (DTZ) against injury induced by isoproterenol using a freely moving rat model in vivo. Sprague Dawley rats were injected subcutaneously (sc) with either 5 or 10 mg/kg of DTZ, or saline as control, twice daily for five doses. One hour after the last injection, a single dose of isoproterenol (30 mg/kg) was injected sc to each rat. Blood samples were collected serially for 6 h for measurement of adenine nucleotides (ATP, ADP and AMP) in red blood cell (RBC) by a validated HPLC. The study has shown isoproterenol induced 50% mortality and also increased RBC concentrations of AMP from 0.04 ± 0.02 to 0.29 ± 0.21 mM at the end of the experiment (p < 0.05). Treatment with 10 mg/kg of DTZ reduced mortality from 50% to <20% and attenuated the increase of RBC concentrations of AMP from +0.25 ± 0.22 in the control rats to +0.072 ± 0.092 mM (p < 0.05). The study concluded that 10 mg/kg of DTZ reduced mortality and breakdown of ATP induced by isoproterenol in rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Cardiovascular Injury on Catabolism of Adenosine and Adenosine 5-'Triphosphate in Systemic Blood in a Freely Moving Rat Model In Vivo.Drug Metab Lett. 2016;10(3):219-226. doi: 10.2174/1872312810666160607013859. Drug Metab Lett. 2016. PMID: 27280599
-
A Pilot Study to Assess Adenosine 5'-triphosphate Metabolism in Red Blood Cells as a Drug Target for Potential Cardiovascular Protection.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2016;15(3):224-32. doi: 10.2174/1871529x15666151102102702. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26521884 Free PMC article.
-
Hemodynamic Assessment and In vivo Catabolism of Adenosine 5'-triphosphate in Doxorubicin or Isoproterenol-induced Cardiovascular Toxicity.Drug Metab Lett. 2021;14(1):80-88. doi: 10.2174/1872312814666201022103802. Drug Metab Lett. 2021. PMID: 33092518
-
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of diltiazem in rats: comparing single vs repeated subcutaneous injections in vivo.Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2007 Oct;28(7):403-7. doi: 10.1002/bdd.568. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2007. PMID: 17668417
-
Long-acting diltiazem HCl for the chronotherapeutic treatment of hypertension and chronic stable angina pectoris.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 May;6(5):765-76. doi: 10.1517/14656566.6.5.765. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 15934903 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine 5'-Triphosphate Metabolism in Red Blood Cells as a Potential Biomarker for Post-Exercise Hypotension and a Drug Target for Cardiovascular Protection.Metabolites. 2018 May 2;8(2):30. doi: 10.3390/metabo8020030. Metabolites. 2018. PMID: 29724022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neutel J.M. Long-term blood pressure control: What can we do? Postgrad. Med. 2011;123:88–93. - PubMed
-
- Mourad J.J., Le Jeune S., Pirollo A., Mourad C., Gaudouen Y., Lopez-Sublet M. Combinations of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system with calcium channel blockers for the treatment of hypertension: Focus on perindopril/amlodipine. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010;26:2263–2276. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama A., Nakano D., Hitomi H. [Calcium antagonists: Current and future applications based on new evidence. Effects of calcium channel blockers on oxidative stress] Clin. Calcium. 2010;20:38–44. - PubMed
-
- Morimoto Y., Kureishi-Bando Y., Murohara T. Calcium antagonists: Current and future applications based on new evidence. Pleiotropic effects of calcium channel blockers on vascular endothelial function. Clin. Calcium. 2010;20:69–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

