Titanium dioxide nanoparticles as guardian against environmental carcinogen benzo[alpha]pyrene
- PMID: 25215666
- PMCID: PMC4162557
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107068
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles as guardian against environmental carcinogen benzo[alpha]pyrene
Abstract
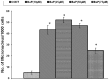
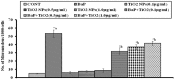
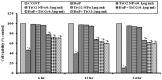
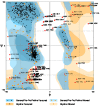
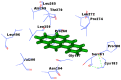
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), like Benzo[alpha]Pyrene (BaP) are known to cause a number of toxic manifestations including lung cancer. As Titanium dioxide Nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) have recently been shown to adsorb a number of PAHs from soil and water, we investigated whether TiO2 NPs could provide protection against the BaP induced toxicity in biological system. A549 cells when co-exposed with BaP (25 µM, 50 µM and 75 µM) along with 0.1 µg/ml,0.5 µg/ml and 1 µg/ml of TiO2 NPs, showed significant reduction in the toxic effects of BaP, as measured by Micronucleus Assay, MTT Assay and ROS Assay. In order to explore the mechanism of protection by TiO2 NP against BaP, we performed in silico studies. BaP and other PAHs are known to enter the cell via aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). TiO2 NP showed a much higher docking score with AHR (12074) as compared to the docking score of BaP with AHR (4600). This indicates a preferential binding of TiO2 NP with the AHR, in case if both the TiO2 NP and BaP are present. Further, we have done the docking of BaP with the TiO2 NP bound AHR-complex (score 4710), and observed that BaP showed strong adsorption on TiO2 NP itself, and not at its original binding site (at AHR). TiO2 NPs thereby prevent the entry of BaP in to the cell via AHR and hence protect cells against the deleterious effects induced by BaP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles provide protection against polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon BaP and chrysene-induced perturbation of DNA repair machinery: A computational biology approach.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2016 Jul;63(4):497-513. doi: 10.1002/bab.1388. Epub 2015 Dec 31. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2016. PMID: 25913286
-
AHR/ROS-mediated mitochondria apoptosis contributes to benzo[a]pyrene-induced heart defects and the protective effects of resveratrol.Toxicology. 2021 Oct;462:152965. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152965. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Toxicology. 2021. PMID: 34597721
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent induction of the IgA receptor FcαRI by the environmental contaminant benzo(a)pyrene in human macrophages.Toxicology. 2011 Nov 28;290(1):89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2011.08.018. Epub 2011 Sep 3. Toxicology. 2011. PMID: 21911031
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Selected Substances Involved in the Reduction of Benzo[a]pyrene-Induced Oxidative Stress.Molecules. 2022 Feb 18;27(4):1379. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041379. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35209168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insight into the Role of AhR in Lung Carcinogenesis.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022 Nov;87(11):1219-1225. doi: 10.1134/S0006297922110013. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022. PMID: 36509717 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticled Titanium Dioxide to Remediate Crude Oil Exposure. An In Vivo Approach in Dicentrarchus labrax.Toxics. 2022 Feb 26;10(3):111. doi: 10.3390/toxics10030111. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35324736 Free PMC article.
-
Individual and combined toxicity of carboxylic acid functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and benzo a pyrene in lung adenocarcinoma cells.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 May;26(13):12709-12719. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04795-x. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30879234
-
Unravelling the Potential Cytotoxic Effects of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles and Metal(Loid) Mixtures on A549 Human Cell Line.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Mar 2;10(3):447. doi: 10.3390/nano10030447. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32131449 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an integrated approach for comparison of in vitro and in vivo responses to particulate matter.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016 Aug 12;13(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12989-016-0152-6. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27520027 Free PMC article.
-
Genotoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Four Different Human Cell Lines (A549, HEPG2, A172 and SH-SY5Y).Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Feb 27;10(3):412. doi: 10.3390/nano10030412. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32120981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denissenko MF, Pao A, Tang M, Pfeifer GP (1996) Preferential formation of benzo[a]pyrene adducts at lung cancer mutational hotspots in P53. Science 274: 430–432. - PubMed
-
- Yoichi N, Xin-Hai P, Koichi T, Feng B, Miiru I, et al. (2000) Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Carcinogens Increase Ubiquitination of p21 Protein after the Stabilization of p53 and the Expression of p2. Am. J. Respir Cell Mol. Biol 22: 747–754. - PubMed
-
- Hsu GW, Huang X, Luneva NP, Geacintov NE, Beese LS (2005) Structure of a High Fidelity DNA Polymerase Bound to a Benzo[a]pyrene Adduct That Blocks Replication. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 280: 3764–3770. - PubMed
-
- Petry T, Schmid P, Schlatter C (1996) The use of toxic equivalency factors in assessing occupational and environmental health risk associated with exposure to airborne mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Chemosphere 32: 639–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

