Foramen ovale closure is a process of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition leading to fibrosis
- PMID: 25215881
- PMCID: PMC4162597
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107175
Foramen ovale closure is a process of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition leading to fibrosis
Abstract
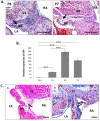
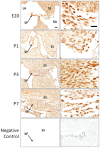
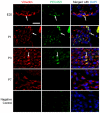
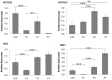
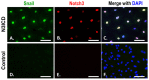
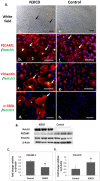
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an atrial septal deformity present in around 25% of the general population. PFO is associated with major causes of morbidity, including stroke and migraine. PFO appears to be heritable but genes involved in the closure of foramen ovale have not been identified. The aim of this study is to determine molecular pathways and genes that are responsible to the postnatal closure of the foramen ovale. Using Sprague-Dawley rat hearts as a model we analysed the dynamic histological changes and gene expressions at the foramen ovale region between embryonic day 20 and postnatal day 7. We observed a gradual loss of the endothelial marker PECAM1, an upregulation of the mesenchymal marker vimentin and α-smooth muscle actin, the elevation of the transcription factor Snail, and an increase of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) in the foramen ovale region as well as the deposition of collagen-rich connective tissues at the closed foramen ovale, suggesting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) occurring during foramen ovale closure which leads to fibrosis. In addition, Notch1 and Notch3 receptors, Notch ligand Jagged1 and Notch effector HRT1 were highly expressed in the endocardium of the foramen ovale region during EndMT. Activation of Notch3 alone in an endothelial cell culture model was able to drive EndMT and transform endothelial cells to mesenchymal phenotype. Our data demonstrate for the first time that FO closure is a process of EndMT-mediated fibrosis, and Notch signalling is an important player participating in this process. Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms of the closure of foramen ovale informs the pathogenesis of PFO and may provide potential options for screening and prevention of PFO related conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Hagen PT, Scholz DG, Edwards WD (1984) Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: an autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin Proc 59: 17–20. - PubMed
-
- Kizer JR, Devereux RB (2005) Clinical practice. Patent foramen ovale in young adults with unexplained stroke. N Engl J Med 353: 2361–2372. - PubMed
-
- Iguchi Y, Kimura K, Kobayashi K, Tachi T, Aihara T, et al. (2008) Sudden deafness and right-to-left shunts. Cerebrovasc Dis 26: 409–412. - PubMed
-
- Moon RE, Camporesi EM, Kisslo JA (1989) Patent foramen ovale and decompression sickness in divers. Lancet 1: 513–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

