Roles of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II in long-term memory formation in crickets
- PMID: 25215889
- PMCID: PMC4162583
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107442
Roles of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II in long-term memory formation in crickets
Abstract
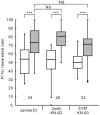
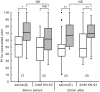
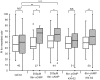
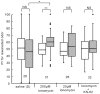
Ca(2+)/calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a key molecule in many systems of learning and memory in vertebrates, but roles of CaMKII in invertebrates have not been characterized in detail. We have suggested that serial activation of NO/cGMP signaling, cyclic nucleotide-gated channel, Ca(2+)/CaM and cAMP signaling participates in long-term memory (LTM) formation in olfactory conditioning in crickets, and here we show participation of CaMKII in LTM formation and propose its site of action in the biochemical cascades. Crickets subjected to 3-trial conditioning to associate an odor with reward exhibited memory that lasts for a few days, which is characterized as protein synthesis-dependent LTM. In contrast, animals subjected to 1-trial conditioning exhibited memory that lasts for only several hours (mid-term memory, MTM). Injection of a CaMKII inhibitor prior to 3-trial conditioning impaired 1-day memory retention but not 1-hour memory retention, suggesting that CaMKII participates in LTM formation but not in MTM formation. Animals injected with a cGMP analogue, calcium ionophore or cAMP analogue prior to 1-trial conditioning exhibited 1-day retention, and co-injection of a CaMKII inhibitor impaired induction of LTM by the cGMP analogue or that by the calcium ionophore but not that by the cAMP analogue, suggesting that CaMKII is downstream of cGMP production and Ca(2+) influx and upstream of cAMP production in biochemical cascades for LTM formation. Animals injected with an adenylyl cyclase (AC) activator prior to 1-trial conditioning exhibited 1-day retention. Interestingly, a CaMKII inhibitor impaired LTM induction by the AC activator, although AC is expected to be a downstream target of CaMKII. The results suggest that CaMKII interacts with AC to facilitate cAMP production for LTM formation. We propose that CaMKII serves as a key molecule for interplay between Ca(2+) signaling and cAMP signaling for LTM formation, a new role of CaMKII in learning and memory.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signaling Pathways for Long-Term Memory Formation in the Cricket.Front Psychol. 2018 Jun 22;9:1014. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01014. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29988479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of NO signaling in long-term memory formation in visual learning in an insect.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 24;8(7):e68538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068538. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894314 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of nitric oxide-cGMP cascade in the formation of cAMP-dependent long-term memory.Learn Mem. 2006 Jan-Feb;13(1):35-44. doi: 10.1101/lm.130506. Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 16452652 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, calmodulin, adenylyl cyclase, and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II are required for late, but not early, long-term memory formation in the honeybee.Learn Mem. 2014 Apr 16;21(5):272-86. doi: 10.1101/lm.032037.113. Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24741108 Free PMC article.
-
Role of signal transduction crosstalk between adenylyl cyclase and MAP kinase in hippocampus-dependent memory.Learn Mem. 2012 Aug 16;19(9):369-74. doi: 10.1101/lm.027128.112. Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22904367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toward elucidating diversity of neural mechanisms underlying insect learning.Zoological Lett. 2015 Feb 10;1:8. doi: 10.1186/s40851-014-0008-6. eCollection 2015. Zoological Lett. 2015. PMID: 26605053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Octopamine and Dopamine Neurons for Mediating Appetitive and Aversive Signals in Pavlovian Conditioning in Crickets.Front Physiol. 2017 Dec 12;8:1027. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01027. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29311961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical roles of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in olfactory memory formation and retrieval in crickets.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 9;15:1345397. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1345397. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38405118 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II is a Ubiquitous Molecule in Human Long-term Memory Synaptic Plasticity: A Systematic Review.Int J Prev Med. 2015 Sep 8;6:88. doi: 10.4103/2008-7802.164831. eCollection 2015. Int J Prev Med. 2015. PMID: 26445635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling Pathways for Long-Term Memory Formation in the Cricket.Front Psychol. 2018 Jun 22;9:1014. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01014. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29988479 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lisman J, Schulman H, Cline H (2002) The molecular basis of CaMKII function in synaptic and behavioural memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 175–190. - PubMed
-
- Silva AJ, Paylor R, Wehner JM, Tonegawa S (1992a) Deficient hippocampal long-term potentiation in α-calcium-calmodulin Kinase II mutant mice. Science 257: 201–206. - PubMed
-
- Silva AJ, Stevens CF, Tonegawa S, Wang Y (1992b) Impaired spatial learning in α-calcium-calmodulin Kinase II mutant mice. Science 257: 206–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

