Roles of Calcium Regulating MicroRNAs in Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 25216032
- PMCID: PMC4197635
- DOI: 10.3390/cells3030899
Roles of Calcium Regulating MicroRNAs in Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
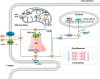
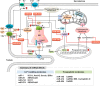
Cardiac Ca2+ cycling and signaling are closely associated with cardiac function. Changes in cellular Ca2+ homeostasis may lead to aberrant cardiac rhythm and may play a critical role in the pathogenesis of cardiac diseases, due to their exacerbation of heart failure. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a key role in the regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level and participate in regulating diverse biological processes. The emerging evidence indicates that the expression profiles of miRNAs vary among human diseases, including cardiovascular diseases. Cardiac Ca2+-handling and signaling proteins are also regulated by miRNAs. Given the relationship between cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis and signaling and miRNA, Ca2+-related miRNAs may serve as therapeutic targets during the treatment of heart failure. In this review, we summarize the knowledge currently available regarding the role of Ca2+ in cardiac function, as well as changes in Ca2+ cycling and homeostasis and the handling of these processes by miRNAs during cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs regulate mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion-injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:1635-1644. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.073. Epub 2016 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27829552 Review.
-
MicroRNA regulation and cardiac calcium signaling: role in cardiac disease and therapeutic potential.Circ Res. 2014 Feb 14;114(4):689-705. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.301798. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24526675 Review.
-
Roles of MicroRNAs in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in the Heart.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jul 22;8:716213. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.716213. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34368265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: a novel promising therapeutic target for cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury?Neural Regen Res. 2015 Nov;10(11):1799-808. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.170302. Neural Regen Res. 2015. PMID: 26807114 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cardiac renin-angiotensin system in sarcoplasmic reticulum function and gene expression in the ischemic-reperfused heart.Mol Cell Biochem. 2000 Sep;212(1-2):227-35. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11108155
Cited by
-
Identification of differential microRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with major depressive disorder.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 12;10(3):e0121975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121975. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25763923 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Long Non-coding RNAs and MicroRNAs in Heart Disease: Insight Into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 10;11:798. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00798. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32754048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulated miR-18b-5p triggers apoptosis by inhibition of calcium signaling and neuronal cell differentiation in transgenic SOD1 (G93A) mice and SOD1 (G17S and G86S) ALS patients.Transl Neurodegener. 2020 Jul 1;9(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00203-4. Transl Neurodegener. 2020. PMID: 32605607 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs in Cardiac Hypertrophy and Heart Failure.Cells. 2022 Feb 23;11(5):777. doi: 10.3390/cells11050777. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction: The Link with Cardiac Arrhythmogenesis.Front Physiol. 2016 Aug 3;7:313. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00313. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27536244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

