Involvement of the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway and XBP1s-dependent transcriptional reprogramming in metabolic diseases
- PMID: 25216212
- PMCID: PMC4281841
- DOI: 10.1089/dna.2014.2552
Involvement of the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway and XBP1s-dependent transcriptional reprogramming in metabolic diseases
Abstract
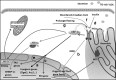
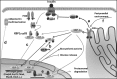
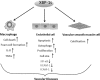
The X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) is not only an important component of the unfolded protein response (UPR), but also an important nuclear transcription factor. Upon endoplasmic reticulum stress, XBP1 is spliced by inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1), thereby generating functional spliced XBP1 (XBP1s). XBP1s functions by translocating into the nucleus to initiate transcriptional programs that regulate a subset of UPR- and non-UPR-associated genes involved in the pathophysiological processes of various diseases. Recent reports have implicated XBP1 in metabolic diseases. This review summarizes the effects of XBP1-mediated regulation on lipid metabolism, glucose metabolism, obesity, and atherosclerosis. Additionally, for the first time, we present XBP1s-dependent transcriptional reprogramming in metabolic diseases under different conditions, including pathology and physiology. Understanding the function of XBP1 in metabolic diseases may provide a basic knowledge for the development of novel therapeutic targets for ameliorating these diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Acosta-Alvear D., Zhou Y., Blais A., Tsikitis M., Lents N.H., Arias C., Lennon C.J., Kluger Y., and Dynlacht B.D. (2007). XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Mol Cell 27,53–66 - PubMed
-
- Benhamron S., Hadar R., Iwawaky T., So J.S., Lee A.H., and Tirosh B. (2014). Regulated IRE1-dependent decay participates in curtailing immunoglobulin secretion from plasma cells. Eur J Immunol 44,867–876 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

