Genetic diversity of livestock-associated MRSA isolates obtained from piglets from farrowing until slaughter age on four farrow-to-finish farms
- PMID: 25217275
- PMCID: PMC4189174
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-014-0089-4
Genetic diversity of livestock-associated MRSA isolates obtained from piglets from farrowing until slaughter age on four farrow-to-finish farms
Abstract
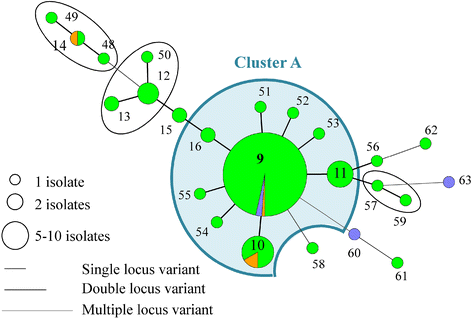
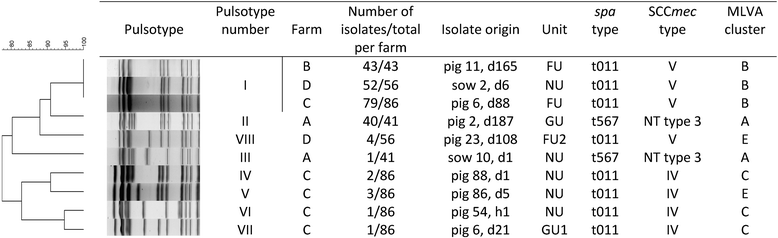
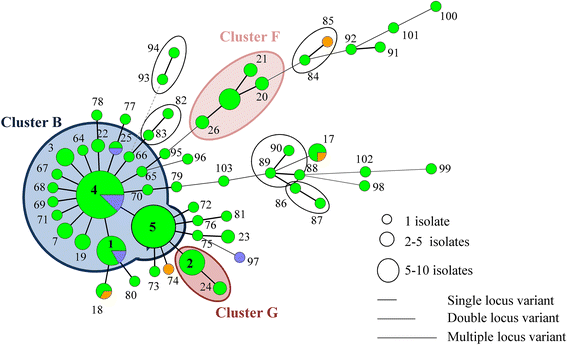
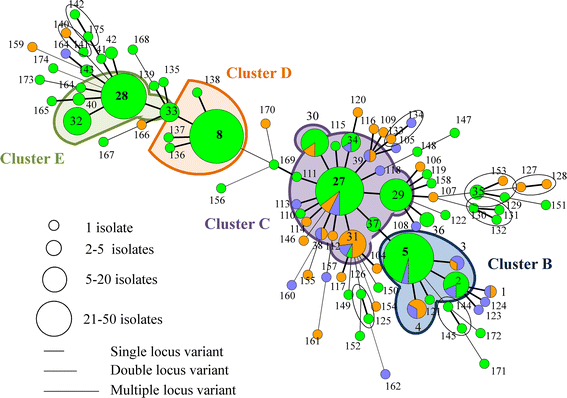
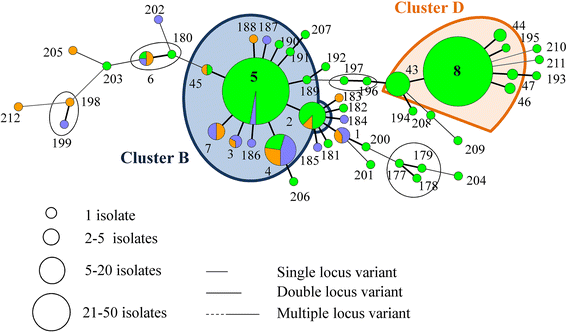
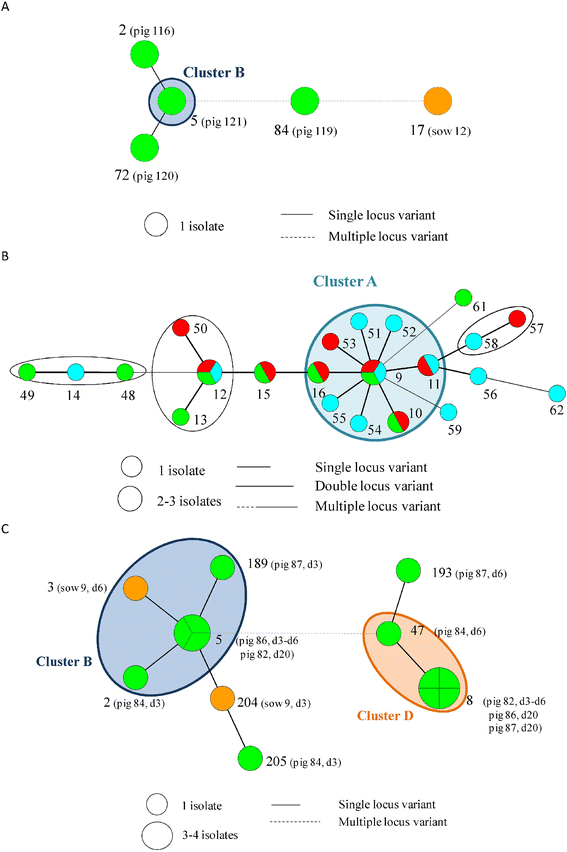
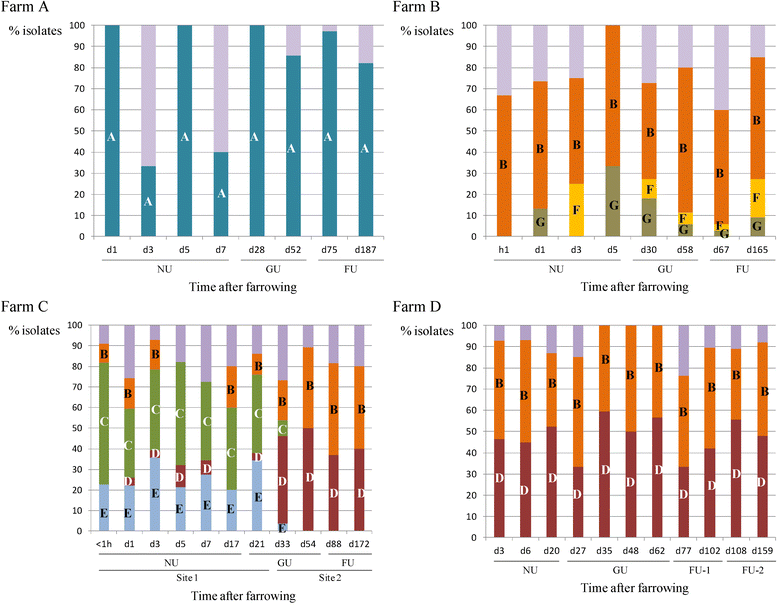
During a previous longitudinal study, performed on four farrow-to-finish farms (A to D), samples were taken from twelve sows, their offspring, and the environment on various occasions over six months to study the MRSA presence. During the present study, a selection of the obtained MRSA isolates were typed by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis (MLVA), Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE), spa typing, and SCCmec typing to study the genetic diversity of LA-MRSA isolates and to determine possible MRSA sources for pig(let)s. PFGE, spa typing, and SCCmec typing revealed the presence of one or few dominant genotype(s) per farm. In contrast, 212 MLVA types were detected on the four farms, forming one cluster on farm A, three on farm B, four on farm C and two on farm D. The genotype, found on farm A was unique for this farm. Farms B, C and D shared one cluster. In general, MLVA types from these clusters were isolated from piglets, sows, and the environment on various sampling events. Piglets carried MLVA types both related and unrelated to their mother sows' MLVA types at farrowing and onwards. In conclusion, molecular typing revealed that within a farm one or a few dominant strain(s) are widespread. Potential MRSA sources for piglets were mother sows, the environment and other piglets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ST398 in pig farms and multispecies farms.Zoonoses Public Health. 2013 Aug;60(5):366-74. doi: 10.1111/zph.12007. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Zoonoses Public Health. 2013. PMID: 22925210
-
Evidence of possible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 spread between pigs and other animals and people residing on the same farm.Prev Vet Med. 2013 May 1;109(3-4):293-303. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2012.10.019. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Prev Vet Med. 2013. PMID: 23200313
-
Epidemiology and genotypic characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains of porcine origin.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Nov;50(11):3687-93. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01971-12. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22972820 Free PMC article.
-
Cohort study for the presence of livestock-associated MRSA in piglets: effect of sow status at farrowing and determination of the piglet colonization age.Vet Microbiol. 2013 Mar 23;162(2-4):679-686. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.09.014. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23067724
-
Characterization of pig-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Mar;201:183-187. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Jan 22. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28284608
Cited by
-
A mechanistic model for spread of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) within a pig herd.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 28;12(11):e0188429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188429. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29182655 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and Epidemiology.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018 Sep 12;31(4):e00020-18. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00020-18. Print 2018 Oct. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30209034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

