Suprachiasmatic nucleus function and circadian entrainment are modulated by G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying (GIRK) channels
- PMID: 25217379
- PMCID: PMC4259544
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.282079
Suprachiasmatic nucleus function and circadian entrainment are modulated by G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying (GIRK) channels
Abstract
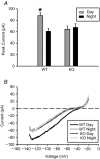
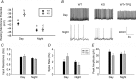
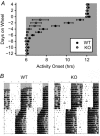
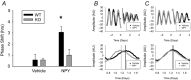
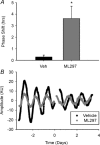
G protein signalling within the central circadian oscillator, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), is essential for conveying time-of-day information. We sought to determine whether G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs) modulate SCN physiology and circadian behaviour. We show that GIRK current and GIRK2 protein expression are greater during the day. Pharmacological inhibition of GIRKs and genetic loss of GIRK2 depolarized the day-time resting membrane potential of SCN neurons compared to controls. Behaviourally, GIRK2 knockout (KO) mice failed to shorten free running period in response to wheel access in constant darkness and entrained more rapidly to a 6 h advance of a 12 h:12 h light-dark (LD) cycle than wild-type (WT) littermate controls. We next examined whether these effects were due to disrupted signalling of neuropeptide Y (NPY), which is known to mediate non-photic phase shifts, attenuate photic phase shifts and activate GIRKs. Indeed, GIRK2 KO SCN slices had significantly fewer silent cells in response to NPY, likely contributing to the absence of NPY-induced phase advances of PER2::LUC rhythms in organotypic SCN cultures from GIRK2 KO mice. Finally, GIRK channel activation is sufficient to cause a non-photic-like phase advance of PER2::LUC rhythms on a Per2(Luc+/-) background. These results suggest that rhythmic regulation of GIRK2 protein and channel function in the SCN contributes to day-time resting membrane potential, providing a mechanism for the fine tuning responses to non-photic and photic stimuli. Further investigation could provide insight into disorders with circadian disruption comorbidities such as epilepsy and addiction, in which GIRK channels have been implicated.
© 2014 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2014 The Physiological Society.
Figures


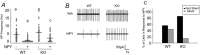
References
-
- Acuna-Goycolea C, Tamamaki N, Yanagawa Y, Obata K. van den Pol AN. Mechanisms of neuropeptide Y, peptide YY, and pancreatic polypeptide inhibition of identified green fluorescent protein-expressing GABA neurons in the hypothalamic neuroendocrine arcuate nucleus. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7406–7419. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguado C, Colon J, Ciruela F, Schlaudraff F, Cabanero MJ, Perry C, Watanabe M, Liss B, Wickman K. Lujan R. Cell type-specific subunit composition of G protein-gated potassium channels in. J Neurochem. 2008;105:497–511. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht U. Timing to perfection: the biology of central and peripheral circadian clocks. Neuron. 2012;74:246–260. - PubMed
-
- Arora D, Hearing M, Haluk DM, Mirkovic K, Fajardo-Serrano A, Wessendorf MW, Watanabe M, Lujan R. Wickman K. Acute cocaine exposure weakens GABAB receptor-dependent G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ signaling in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci. 2011;31:12251–12257. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

