Interferon receptor signaling in malignancy: a network of cellular pathways defining biological outcomes
- PMID: 25217450
- PMCID: PMC4272667
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0450
Interferon receptor signaling in malignancy: a network of cellular pathways defining biological outcomes
Abstract
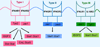
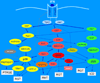
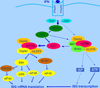
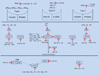
IFNs are cytokines with important antiproliferative activity and exhibit key roles in immune surveillance against malignancies. Early work initiated over three decades ago led to the discovery of IFN receptor activated Jak-Stat pathways and provided important insights into mechanisms for transcriptional activation of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG) that mediate IFN biologic responses. Since then, additional evidence has established critical roles for other receptor-activated signaling pathways in the induction of IFN activities. These include MAPK pathways, mTOR cascades, and PKC pathways. In addition, specific miRNAs appear to play a significant role in the regulation of IFN signaling responses. This review focuses on the emerging evidence for a model in which IFNs share signaling elements and pathways with growth factors and tumorigenic signals but engage them in a distinctive manner to mediate antiproliferative and antiviral responses.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon signaling in cancer. Non-canonical pathways and control of intracellular immune checkpoints.Semin Immunol. 2019 Jun;43:101299. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2019.101299. Semin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31771762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of type I interferon signaling in normal and malignant cells.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2004 May-Jun;52(3):156-63. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2004. PMID: 15247882 Review.
-
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and its role in interferon signaling.Pharmacol Ther. 2003 May;98(2):129-42. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(03)00016-0. Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12725866 Review.
-
Novel type III interferons produce anti-tumor effects through multiple functions.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jun 1;18(3):909-18. doi: 10.2741/4152. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23747856 Review.
-
Role of the intracellular domain of the human type I interferon receptor 2 chain (IFNAR2c) in interferon signaling. Expression of IFNAR2c truncation mutants in U5A cells.J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 4;275(31):23981-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002518200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10825167
Cited by
-
Sirtuin 2-mediated deacetylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 promotes STAT1 signaling in type I interferon responses.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jan 18;294(3):827-837. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005956. Epub 2018 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30487288 Free PMC article.
-
Type I and II Interferons in the Anti-Tumor Immune Response.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 2;13(5):1037. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051037. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary cilia contribute to the aggressiveness of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 20;13(9):806. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05243-4. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36127323 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon signaling in cancer. Non-canonical pathways and control of intracellular immune checkpoints.Semin Immunol. 2019 Jun;43:101299. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2019.101299. Semin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31771762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of expression profiles between undifferentiated and differentiated porcine IPEC-J2 cells.Porcine Health Manag. 2022 Jan 9;8(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40813-022-00247-0. Porcine Health Manag. 2022. PMID: 35000622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hofmann WP, Zeuzem S. A new standard of care for the treatment of chronic HCV infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011;8:257–264. - PubMed
-
- Rönnblom L, Eloranta ML. The interferon signature in autoimmune diseases. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2013;25:248–253. - PubMed
-
- Wahren-Herlenius M, Dörner T. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of systemic autoimmune disease. Lancet. 2013;382:819–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

