Off-target effects of the septin drug forchlorfenuron on nonplant eukaryotes
- PMID: 25217460
- PMCID: PMC4248692
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00191-14
Off-target effects of the septin drug forchlorfenuron on nonplant eukaryotes
Abstract
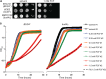
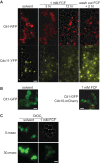
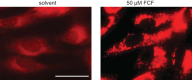
The septins are a family of GTP-binding proteins that form cytoskeletal filaments. Septins are highly conserved and evolutionarily ancient but are absent from land plants. The synthetic plant cytokinin forchlorfenuron (FCF) was shown previously to inhibit budding yeast cell division and induce ectopic septin structures (M. Iwase, S. Okada, T. Oguchi, and A. Toh-e, Genes Genet. Syst. 79:199-206, 2004, http://dx.doi.org/10.1266/ggs.79.199). Subsequent studies in a wide range of eukaryotes have concluded that FCF exclusively inhibits septin function, yet the mechanism of FCF action in nonplant cells remains poorly understood. Here, we report that the cellular effects of FCF are far more complex than previously described. The reported growth arrest of budding yeast cells treated with 1 mM FCF partly reflects sensitization caused by a bud4 mutation present in the W303 strain background. In wild-type (BUD4(+)) budding yeast, growth was inhibited at FCF concentrations that had no detectable effect on septin structure or function. Moreover, FCF severely inhibited the proliferation of fission yeast cells, in which septin function is nonessential. FCF induced fragmentation of budding yeast mitochondrial reticula and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Mitochondria also fragmented in cultured mammalian cells treated with concentrations of FCF that previously were assumed to target septins only. Finally, FCF potently inhibited ciliation and motility and induced mitochondrial disorganization in Tetrahymena thermophila without apparent alterations in septin structure. None of these effects was consistent with the inhibition of septin function. Our findings point to nonseptin targets as major concerns when using FCF.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Septin Cytoskeleton-Targeting Small Molecule, Forchlorfenuron, Inhibits Epithelial Migration via Septin-Independent Perturbation of Cellular Signaling.Cells. 2019 Dec 29;9(1):84. doi: 10.3390/cells9010084. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31905721 Free PMC article.
-
Forchlorfenuron alters mammalian septin assembly, organization, and dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 24;283(43):29563-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804962200. Epub 2008 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18713753 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular requirements for the small molecule forchlorfenuron to stabilize the septin cytoskeleton.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010 Jun;67(6):383-99. doi: 10.1002/cm.20452. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010. PMID: 20517926
-
Reuse, replace, recycle. Specificity in subunit inheritance and assembly of higher-order septin structures during mitotic and meiotic division in budding yeast.Cell Cycle. 2009 Jan 15;8(2):195-203. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.2.7381. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19164941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding post-translational modifications of mammalian septins.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2023 Jul-Aug;80(7-8):169-181. doi: 10.1002/cm.21747. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 36797225 Review.
Cited by
-
A Septin Cytoskeleton-Targeting Small Molecule, Forchlorfenuron, Inhibits Epithelial Migration via Septin-Independent Perturbation of Cellular Signaling.Cells. 2019 Dec 29;9(1):84. doi: 10.3390/cells9010084. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31905721 Free PMC article.
-
The phytohormone forchlorfenuron decreases viability and proliferation of malignant mesothelioma cells in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2019 Dec 10;10(65):6944-6956. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27341. eCollection 2019 Dec 10. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31857849 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Potent Forchlorfenuron Analogs and Their Cytotoxic Effect in Cancer Cell Lines.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 24;10(1):3241. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59824-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32094384 Free PMC article.
-
Migration of Myogenic Cells Is Highly Influenced by Cytoskeletal Septin7.Cells. 2023 Jul 11;12(14):1825. doi: 10.3390/cells12141825. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508490 Free PMC article.
-
Saccharomyces spores are born prepolarized to outgrow away from spore-spore connections and penetrate the ascus wall.Yeast. 2021 Jan;38(1):90-101. doi: 10.1002/yea.3540. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Yeast. 2021. PMID: 33238051 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

