Targeted noninvasive imaging of EGFR-expressing orthotopic pancreatic cancer using multispectral optoacoustic tomography
- PMID: 25217521
- PMCID: PMC4216771
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1656
Targeted noninvasive imaging of EGFR-expressing orthotopic pancreatic cancer using multispectral optoacoustic tomography
Abstract
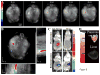
Detection of orthotopic xenograft tumors is difficult due to poor spatial resolution and reduced image fidelity with traditional optical imaging modalities. In particular, light scattering and attenuation in tissue at depths beyond subcutaneous implantation hinder adequate visualization. We evaluate the use of multispectral optoacoustic tomography (MSOT) to detect upregulated epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor in orthotopic pancreatic xenografts using a near-infrared EGF-conjugated CF-750 fluorescent probe. MSOT is based on the photoacoustic effect and thus not limited by photon scattering, resulting in high-resolution tomographic images. Pancreatic tumor-bearing mice with luciferase-transduced S2VP10L tumors were intravenously injected with EGF-750 probe before MSOT imaging. We characterized probe specificity and bioactivity via immunoblotting, immunocytochemistry, and flow cytometric analysis. In vitro data along with optical bioluminescence/fluorescence imaging were used to validate acquired MSOT in vivo images of probe biodistribution. Indocyanine green dye was used as a nonspecific control to define specificity of EGF-probe accumulation. Maximum accumulation occurred at 6 hours postinjection, demonstrating specific intratumoral probe uptake and minimal liver and kidney off-target accumulation. Optical bioluminescence and fluorescence imaging confirmed tumor-specific probe accumulation consistent with MSOT images. These studies demonstrate the utility of MSOT to obtain volumetric images of ligand probe biodistribution in vivo to detect orthotopic pancreatic tumor lesions through active targeting of the EGF receptor.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Statement: None
Figures



Similar articles
-
Orthotopic pancreatic tumors detected by optoacoustic tomography using Syndecan-1.J Surg Res. 2015 Jan;193(1):246-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.06.045. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25439222 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Acidity in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography Detects pH-Low Insertion Peptide Probes In Vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 15;21(20):4576-85. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0314. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26124201 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence- and multispectral optoacoustic imaging for an optimized detection of deeply located tumors in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2018 May 15;142(10):2118-2129. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31236. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29277891
-
Deep tissue optical and optoacoustic molecular imaging technologies for pre-clinical research and drug discovery.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012 Mar;13(4):504-22. doi: 10.2174/138920112799436258. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22216767 Review.
-
Development of Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography as a Clinically Translatable Modality for Cancer Imaging.Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2020 Nov 20;2(6):e200066. doi: 10.1148/rycan.2020200066. eCollection 2020 Nov. Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33330850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions Between Tumor Biology and Targeted Nanoplatforms for Imaging Applications.Adv Funct Mater. 2020 May 11;30(19):1910402. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910402. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Adv Funct Mater. 2020. PMID: 34093104 Free PMC article.
-
Activatable probes for diagnosing and positioning liver injury and metastatic tumors by multispectral optoacoustic tomography.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 28;9(1):3983. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06499-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30266905 Free PMC article.
-
piRNA-independent function of PIWIL1 as a co-activator for anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome to drive pancreatic cancer metastasis.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Apr;22(4):425-438. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0486-z. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32203416
-
Small Molecule Optoacoustic Contrast Agents: An Unexplored Avenue for Enhancing In Vivo Imaging.Molecules. 2018 Oct 25;23(11):2766. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112766. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30366395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indocyanine Green-Conjugated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoworm for Multimodality Breast Cancer Imaging.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2022 Dec 23;5(12):18912-18920. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.2c04687. Epub 2022 Dec 5. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2022. PMID: 37635916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pocard M, Tsukui H, Salmon RJ, Dutrillaux B, Poupon MF. Efficiency of orthotopic xenograft models for human colon cancers. In Vivo. 1996;10(5):463–9. - PubMed
-
- Kagadis GC, Loudos G, Katsanos K, Langer SG, Nikiforidis GC. In vivo small animal imaging: current status and future prospects. Med Phys. 2010;37(12):6421–42. - PubMed
-
- Tangney M, Francis KP. In vivo optical imaging in gene & cell therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2012;12(1):2–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

