Deletions in the fifth alpha helix of HIV-1 matrix block virus release
- PMID: 25217711
- PMCID: PMC4253686
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.08.017
Deletions in the fifth alpha helix of HIV-1 matrix block virus release
Abstract
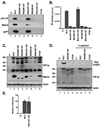
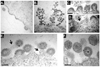
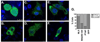
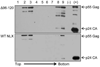
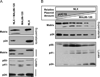
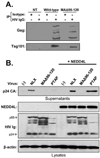
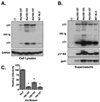
The matrix (MA) protein of HIV-1 is the N-terminal component of the Gag structural protein and is critical for the early and late stages of viral replication. MA contains five α-helices (α1-α5). Deletions in the N-terminus of α5 as small as three amino acids impaired virus release. Electron microscopy of one deletion mutant (MA∆96-120) showed that its particles were tethered to the surface of cells by membranous stalks. Immunoblots indicated all mutants were processed completely, but mutants with large deletions had alternative processing intermediates. Consistent with the EM data, MA∆96-120 retained membrane association and multimerization capability. Co-expression of this mutant inhibited wild type particle release. Alanine scanning mutation in this region did not affect virus release, although the progeny virions were poorly infectious. Combined, these data demonstrate that structural ablation of the α5 of MA inhibits virus release.
Keywords: Deletion mutagenesis; HIV-1 assembly; HIV-1 budding; Matrix; NEDD4L.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abacioglu YH, Fouts TR, Laman JD, Claassen E, Pincus SH, Moore JP, Roby CA, Kamin-Lewis R, Lewis GK. Epitope mapping and topology of baculovirus-expressed HIV-1 gp160 determined with a panel of murine monoclonal antibodies. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994;10(4):371–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

