In vivo detection of hyperoxia-induced pulmonary endothelial cell death using (99m)Tc-duramycin
- PMID: 25218023
- PMCID: PMC4383294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2014.08.010
In vivo detection of hyperoxia-induced pulmonary endothelial cell death using (99m)Tc-duramycin
Abstract
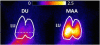
Introduction: (99m)Tc-duramycin, DU, is a SPECT biomarker of tissue injury identifying cell death. The objective of this study is to investigate the potential of DU imaging to quantify capillary endothelial cell death in rat lung injury resulting from hyperoxia exposure as a model of acute lung injury.
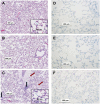
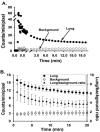
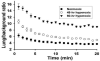
Methods: Rats were exposed to room air (normoxic) or >98% O2 for 48 or 60 hours. DU was injected i.v. in anesthetized rats, scintigraphy images were acquired at steady-state, and lung DU uptake was quantified from the images. Post-mortem, the lungs were removed for histological studies. Sequential lung sections were immunostained for caspase activation and endothelial and epithelial cells.
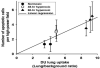
Results: Lung DU uptake increased significantly (p<0.001) by 39% and 146% in 48-hr and 60-hr exposed rats, respectively, compared to normoxic rats. There was strong correlation (r(2)=0.82, p=0.005) between lung DU uptake and the number of cleaved caspase 3 (CC3) positive cells, and endothelial cells accounted for more than 50% of CC3 positive cells in the hyperoxic lungs. Histology revealed preserved lung morphology through 48 hours. By 60 hours there was evidence of edema, and modest neutrophilic infiltrate.
Conclusions: Rat lung DU uptake in vivo increased after just 48 hours of >98% O2 exposure, prior to the onset of any substantial evidence of lung injury. These results suggest that apoptotic endothelial cells are the primary contributors to the enhanced DU lung uptake, and support the utility of DU imaging for detecting early endothelial cell death in vivo.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Apoptosis; Lung imaging.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential lung uptake of 99mTc-hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime and 99mTc-duramycin in the chronic hyperoxia rat model.J Nucl Med. 2012 Dec;53(12):1984-91. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.108498. Epub 2012 Oct 19. J Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 23086010 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo molecular imaging stratifies rats with different susceptibilities to hyperoxic acute lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):L410-L422. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00126.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35943727 Free PMC article.
-
Protection by Inhaled Hydrogen Therapy in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Injury can be Tracked in vivo Using Molecular Imaging.Shock. 2017 Oct;48(4):467-476. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000872. Shock. 2017. PMID: 28915216 Free PMC article.
-
[Apoptosis in neonatal rat lung exposed to hyperoxia].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Aug;43(8):585-90. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16191268 Chinese.
-
Imaging of rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury using(99m)Tc-labeled duramycin.Nucl Med Biol. 2013 Jan;40(1):80-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Nucl Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23123139 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers to Predict Lethal Radiation Injury to the Rat Lung.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 15;24(6):5627. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065627. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982722 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging-based diagnosis of acute renal allograft rejection.World J Transplant. 2016 Mar 24;6(1):174-82. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.174. World J Transplant. 2016. PMID: 27011915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Xenograft After Paclitaxel Treatment With 99mTc-Labeled Duramycin SPECT/CT.Mol Imaging. 2016 Jan 29;15:1536012115624918. doi: 10.1177/1536012115624918. Print 2016. Mol Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27030401 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for Radiation Pneumonitis Using Noninvasive Molecular Imaging.J Nucl Med. 2016 Aug;57(8):1296-301. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.160291. Epub 2016 Mar 31. J Nucl Med. 2016. PMID: 27033892 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Oxidation Protects against Hyperoxia-induced Endothelial Cell Apoptosis and Lung Injury in Neonatal Mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;60(6):667-677. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0335OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30571144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gajic O, Dara SI, Mendez JL, Adesanya AO, Festic E, Caples SM, Rana R, St Sauver JL, Lymp JF, Afessa B, Hubmayr RD. Ventilator-associated lung injury in patients without acute lung injury at the onset of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:1817–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

