The role of bronchial epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of COPD in Z-alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
- PMID: 25218041
- PMCID: PMC4177581
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-014-0112-3
The role of bronchial epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of COPD in Z-alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Abstract
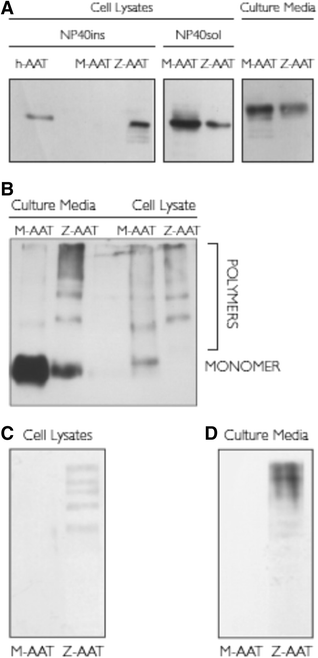
Background: Alpha-1 antitrypsin is the main inhibitor of neutrophil elastase in the lung. Although it is principally synthesized by hepatocytes, alpha-1 antitrypsin is also secreted by bronchial epithelial cells. Gene mutations can lead to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, with the Z variant being the most clinically relevant due to its propensity to polymerize. The ability of bronchial epithelial cells to produce Z-variant protein and its polymers is unknown.
Methods: Experiments using a conformation-specific antibody were carried out on M- and Z-variant-transfected 16HBE cells and on bronchial biopsies and ex vivo bronchial epithelial cells from Z and M homozygous patients. In addition, the effect of an inflammatory stimulus on Z-variant polymer formation, elicited by Oncostatin M, was investigated. Comparisons of groups were performed using t-test or ANOVA. Non-normally distributed data were assessed by Mann-Whitney U test or the Kruskal-Wallis test, where appropriate. A P value of < 0.05 was considered to be significant.
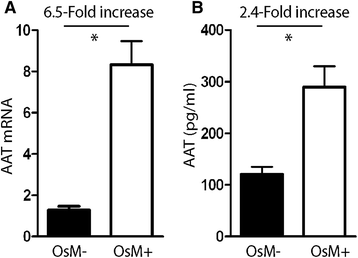
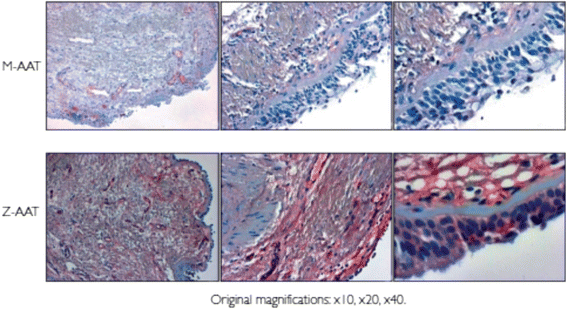
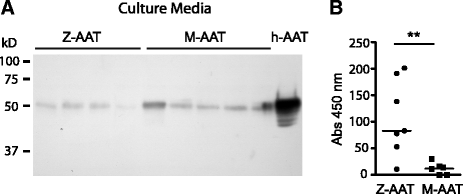
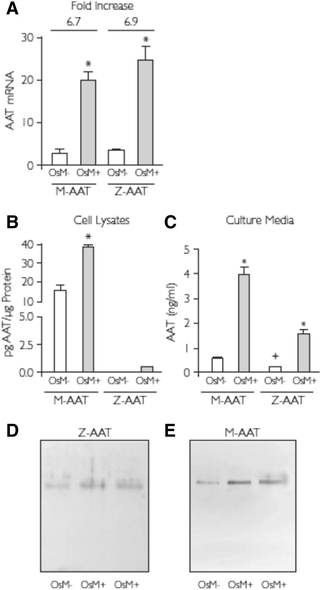
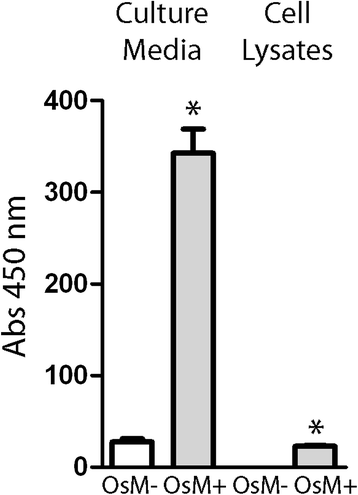
Results: Alpha-1 antitrypsin polymers were found at a higher concentration in the culture medium of ex vivo bronchial epithelial cells from Z-variant homozygotes, compared with M-variant homozygotes (P < 0.01), and detected in the bronchial epithelial cells and submucosa of patient biopsies. Oncostatin M significantly increased the expression of alpha-1 antitrypsin mRNA and protein (P < 0.05), and the presence of Z-variant polymers in ex vivo cells (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Polymers of Z-alpha-1 antitrypsin form in bronchial epithelial cells, suggesting that these cells may be involved in the pathogenesis of lung emphysema and in bronchial epithelial cell dysfunction.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson D, Travis J. Structural evidence for methionine at the reactive site of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:7142–7144. - PubMed
-
- Du Bois RM, Bernaudin JF, Paakko P, Hubbard R, Takahashi H, Ferrans V, Crystal RG. Human neutrophils express the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene and produce alpha 1-antitrypsin. Blood. 1991;77:2724–2730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

