Fronto-parietal network supports context-dependent speech comprehension
- PMID: 25218167
- PMCID: PMC4410787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.09.007
Fronto-parietal network supports context-dependent speech comprehension
Abstract
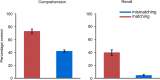
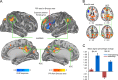
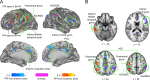
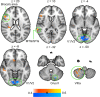
Knowing the context of a discourse is an essential prerequisite for comprehension. Here we used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to disclose brain networks supporting context-dependent speech comprehension. During fMRI, 20 participants listened to 1-min spoken narratives preceded by pictures that were either contextually matching or mismatching with the narrative. Matching pictures increased narrative comprehension, decreased hemodynamic activity in Broca׳s area, and enhanced its functional connectivity with left anterior superior frontal gyrus, bilateral inferior parietal cortex, as well as anterior and posterior cingulate cortex. Further, the anterior (BA 45) and posterior (BA 44) portions of Broca׳s area differed in their functional connectivity patterns. Both BA 44 and BA 45 have shown increased connectivity with right angular gyrus and supramarginal gyrus. Whereas BA 44 showed increased connectivity with left angular gyrus, left inferior/middle temporal gyrus and left postcentral gyrus, BA 45 showed increased connectivity with right posterior cingulate cortex, right anterior inferior frontal gyrus, lateral occipital cortex and anterior cingulate cortex. Our results suggest that a fronto-parietal functional network supports context-dependent narrative comprehension, and that Broca׳s area is involved in resolving ambiguity from speech when appropriate contextual cues are lacking.
Keywords: Broca׳s area; Functional connectivity; ISC; Narrative; PPI; Speech comprehension; Wernicke׳s area; fMRI.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural circuit of verbal humor comprehension in schizophrenia - an fMRI study.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 Jun 3;15:525-540. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.06.005. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 28652967 Free PMC article.
-
Task-modulated activation and functional connectivity of the temporal and frontal areas during speech comprehension.Neuroscience. 2013 May 1;237:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.067. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23357111
-
Comprehension of degraded speech sounds with m-sequence modulation: an fMRI study.Neuroimage. 2010 Feb 1;49(3):2697-706. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.063. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 19878726
-
Neural correlates and network connectivity underlying narrative production and comprehension: a combined fMRI and PET study.Cortex. 2014 Aug;57:107-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2014.01.017. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Cortex. 2014. PMID: 24845161
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of memory-guided attention: Frontal and parietal activation suggests involvement of fronto-parietal networks.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2021 Jan;12(1):e1546. doi: 10.1002/wcs.1546. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2021. PMID: 33099860
Cited by
-
Emotions amplify speaker-listener neural alignment.Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Nov 1;40(16):4777-4788. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24736. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019. PMID: 31400052 Free PMC article.
-
Linguistic processing of task-irrelevant speech at a cocktail party.Elife. 2021 May 4;10:e65096. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65096. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33942722 Free PMC article.
-
Functional network connectivity patterns predicting the efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the spectrum of Alzheimer's disease.Eur Radiol Exp. 2023 Oct 24;7(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s41747-023-00376-3. Eur Radiol Exp. 2023. PMID: 37872457 Free PMC article.
-
High-gamma and beta bursts in the left supramarginal gyrus can differentiate verbal memory states and performance.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1627528. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1627528. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40823292 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting "When" in Discourse Engages the Human Dorsal Auditory Stream: An fMRI Study Using Naturalistic Stories.J Neurosci. 2016 Nov 30;36(48):12180-12191. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4100-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27903727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abutalebi J., Della Rosa P.A., Green D.W., Hernandez M., Scifo P., Keim R. Bilingualism tunes the anterior cingulate cortex for conflict monitoring. Cerebral Cortex. 2012;22(9):2076–2086. - PubMed
-
- Amunts K., Schleicher A., Bürgel U., Mohlberg H., Uylings H.B., Zilles K. Broca׳s region revisited: cytoarchitecture and intersubject variability. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1999;412(2):319–341. - PubMed
-
- Amunts K., Weiss P.H., Mohlberg H., Pieperhoff P., Eickhoff S., Gurd J.M. Analysis of neural mechanisms underlying verbal fluency in cytoarchitectonically defined stereotaxic space—the roles of Brodmann areas 44 and 45. NeuroImage. 2004;22(1):42–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

