Disruption of striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) function in neuropsychiatric disorders
- PMID: 25218562
- PMCID: PMC4259835
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neures.2014.08.018
Disruption of striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) function in neuropsychiatric disorders
Abstract
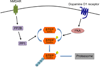
Striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) is a brain-specific tyrosine phosphatase that plays a major role in the development of synaptic plasticity. Recent findings have implicated STEP in several psychiatric and neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, fragile X syndrome, Huntington's disease, stroke/ischemia, and stress-related psychiatric disorders. In these disorders, STEP protein expression levels and activity are dysregulated, contributing to the cognitive deficits that are present. In this review, we focus on the most recent findings on STEP, discuss how STEP expression and activity are maintained during normal cognitive function, and how disruptions in STEP activity contribute to a number of illnesses.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Fragile X syndrome; Huntington's disease; STEP; Schizophrenia; Stroke.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd and the Japan Neuroscience Society. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adachi M, Sekiya M, Arimura Y, Takekawa M, Itoh F, Hinoda Y, Imai K, Yachi A. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase expression in pre-B cell NALM-6. Cancer Res. 1992;52:737–740. - PubMed
-
- Antar LN, Bassell GJ. Sunrise at the synapse: the FMRP mRNP shaping the synaptic interface. Neuron. 2003;37:555–558. - PubMed
-
- Aronowski J, Strong R, Grotta JC. Reperfusion injury: demonstration of brain damage produced by reperfusion after transient focal ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:1048–1056. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Huber KM, Warren ST. The mGluR theory of fragile X mental retardation. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:370–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

