Fronto-striatal circuits in response-inhibition: Relevance to addiction
- PMID: 25218611
- PMCID: PMC4686018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.012
Fronto-striatal circuits in response-inhibition: Relevance to addiction
Abstract
Disruptions to inhibitory control are believed to contribute to multiple aspects of drug abuse, from preexisting vulnerability in at-risk individuals, through escalation to dependence, to promotion of relapse in chronic users. Paradigms investigating the suppression of actions have been investigated in animal and human research on drug addiction. Rodent research has focused largely on impulsive behaviors, often gauged by premature responding, as a viable model highlighting the relevant role of dopamine and other neurotransmitters primarily in the striatum. Human research on action inhibition in stimulant dependence has highlighted impaired performance and largely prefrontal cortical abnormalities as part of a broader pattern of cognitive abnormalities. Animal and human research implicate inhibitory difficulties mediated by fronto-striatal circuitry both preceding and as a result of excessive stimulus use. In this regard, response-inhibition has proven a useful cognitive function to gauge the integrity of fronto-striatal systems and their role in contributing to impulsive and compulsive features of drug dependence.
Keywords: Addiction; Cognitive control; Drug use; Relapse; Stimulant dependence; Stop-signal.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
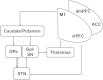
Similar articles
-
Addiction, compulsive drug seeking, and the role of frontostriatal mechanisms in regulating inhibitory control.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010 Nov;35(2):248-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.03.001. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010. PMID: 20223263 Review.
-
Impaired functional connectivity within and between frontostriatal circuits and its association with compulsive drug use and trait impulsivity in cocaine addiction.JAMA Psychiatry. 2015 Jun;72(6):584-92. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.1. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25853901
-
Striatocortical pathway dysfunction in addiction and obesity: differences and similarities.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Jan-Feb;48(1):1-19. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2012.735642. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23173916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in Striatal Circuits Underlying Addiction-Like Behaviors.Mol Cells. 2017 Jun 30;40(6):379-385. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2017.0088. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Mol Cells. 2017. PMID: 28724279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addiction and brain reward and antireward pathways.Adv Psychosom Med. 2011;30:22-60. doi: 10.1159/000324065. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Adv Psychosom Med. 2011. PMID: 21508625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Non-invasive Neuromodulation on Executive and Other Cognitive Functions in Addictive Disorders: A Systematic Review.Front Neurosci. 2018 Sep 19;12:642. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00642. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30283294 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and neurobiological mechanisms of punishment: implications for psychiatric disorders.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jul;43(8):1639-1650. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0047-3. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29703994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validity and utility of Hierarchical Taxonomy of Psychopathology (HiTOP): II. Externalizing superspectrum.World Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;20(2):171-193. doi: 10.1002/wps.20844. World Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34002506 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in tobacco smokers: Executive control network and frontostriatal connectivity.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019 Feb 1;195:59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.11.023. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019. PMID: 30592997 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Methylphenidate as a treatment option for substance use disorder: a transdiagnostic perspective.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Aug 3;14:1208120. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1208120. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37599874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albein-Urios N., Martinez-Gonzalez J.M., Lozano O., Moreno-Lopez L., Soriano-Mas C., Verdejo-Garcia A. Negative urgency, disinhibition and reduced temporal pole gray matter characterize the comorbidity of cocaine dependence and personality disorders. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013;132:231–237. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . vol. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000. (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders).
-
- Anderson A.L., Reid M.S., Li S.H., Holmes T., Shemanski L., Slee A., Smith E.V., Kahn R., Chiang N., Vocci F., Ciraulo D., Dackis C., Roache J.D., Salloum I.M., Somoza E., Urschel H.C., 3rd, Elkashef A.M. Modafinil for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009;104:133–139. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

